System Design
Redis

In-memory key-value data store. Stores cache data into physical storage if needed.
Executes ultra-fast LUA scripts.
Supports blocking queues.
Single threaded: an individual command is always atomic Provide concurrency at the I/O level by I/O multiplexing + even loop. Atomicity is at no extra cost (doesn’t require synchronization between threads) CPU is usually not the bottleneck. IT’s either memory or network bound. Redis 4.0 more threaded: deleting objects in the background, blocking commands implemented via Redis modules
Pipelining (vs batching?) Redis commands
Multi/exec sequence ensures no other clients are executing commands in between.
Transactions: MULTI, EXEC, DISCARD, WATCH Rollback is not supported
Atomicity
CRDTs: Conflict-Free Replicated Data Types
TCP ports
- Redis TCP port: node to clients
- Cluster bus port: node to node
- Redis Cluster Bus
- Binary protocol (Gossip)
- Full mesh
- Propagate information about the cluster
- Discover new nodes
- Send ping packets for failure detection
- Configuration updates
- Failover authorization
- Propagate Pub/Sub messages
---
title: Node handshake
---
sequenceDiagram
Note over Node X, Node B: Even if Node X is untrusted
Node X->>Node B: PING
Node B-->>Node X: PONG/The provided argument
Note over Node A, Node B: Requested by System Admin
Node A->>Node B: CLUSTER MEET ip port
Node B-->>Node A: OK
Node B->>Node C: Gossip message about A
Heartbeat
PINGandPONGpackets- Every node:
- pings a few random nodes every second
- makes sure to ping every other node that hasn’t sent a ping or received a pong for
> NODE_TIMEOUT / 2
---
title: Failure Detection
---
sequenceDiagram
Node A->>Node B: PING
Note left of Node B: No reply after NODE_TIMEOUT / 2
Node A->>Node B: Try to reconnect
Note left of Node B: No reply after NODE_TIMEOUT
Node A->>Node A: Flag Node B PFAIL
Other Nodes-)Node A: Gossip about Node B
Note right of Node A: The majority of Masters flagged Node B PFAIL/FAIL
Note right of Node A: within NODE_TIMEOUT * FAIL_REPORT_VALIDITY_MULT
Node A->>Node A: Flag Node B FAIL
Node A-)Other Nodes: Send FAIL messages
Note over Node A, Other Nodes: NOT a FAIL condition within a heartbeat message
Other Nodes-)Other Nodes: Flag Node B FAIL
---
title: Flag of Node B
---
stateDiagram-v2
[*] --> PFAIL: Unreachable
[*] --> FAIL: FAIL message
PFAIL --> FAIL: Majority agreement or FAIL Message
FAIL --> [*]: Reachable
note right of FAIL
- Replica
- Master Not serving any slot
- Master N * NODE_TIMEOUT has elapsed without detectable replica promotion
end note
Data persistence
- RDB: snapshots
dump.rdbby default- Manual commands:
SAVE/BGSAVE fork()using a child process
- AOF (Append Only Files)
fsyncpolicies- Log rewriting:
BGREWRITAOF - More durable (how much data you can afford to lose)
Scaling
Algorithmic sharding:
1
HASH_SLOT = CRC16(key) mod 16384
hash tags force certain keys to be stored in the same hash slot
---
title: Redirection
---
sequenceDiagram
Client->>Node A: Query <hash_slot>
alt Has <hash_slot>
Node A->>Node A: Process
Node A-->>Client: Reply
else
Node A->>Node A: Look up hash slot to node map
Node A-->>Client: -MOVED <hash_slot> <ip:port>
end
Client->>Client: CLUSTER SHARDS (Update slot configuration map)
Resharding
READONLY: client is OK reading possibly stale data and it not interested in running write queries. Replica nodes will not redirect client to the authoritative master for the hash slot involved in the given command.
---
title: Scaling reads using READONLY
---
sequenceDiagram
Client->>Replica: Read
alt Keys served by the replica's master
Replica-->>Client: Reply
else
Replica-->>Client: -MOVED <hash_slot> <ip:port>
Note over Client, Replica: 1) Never served 2) Resharded
end
Client->>Client: CLUSTER SHARDS
Replication
Replication: Master-replica (Leader-follower)
Asynchronous replication by default.
Not strong consistency!
---
title: Failure Mode 1
---
sequenceDiagram
activate Master
Client->>Master: Write
Master-->>Client: Ack
deactivate Master
Note right of Master: Master failed
Master-xReplica: Replicate
Note right of Replica: Promoted as Master
Note right of Replica: Data loss
Synchronous replication is supported when absolutely needed, via WAIT. But it’s always possible that a replica that was not able to receive the write will be elected as master. So it’s not strong consistency.
Actions that change master dataset:
- client writes
- keys expired or evicted
- others
Master-replica link breaks (due to network issues or timeout): partial resynchronization
---
title: Synchronization
---
sequenceDiagram
Replica->>Master: PSYNC (Replication ID + offset)
alt Partial resynchronization
Master-->>Replica: Incremental part
else Full synchronization
par
Master->>Master: Produce an RDB file
and
Master->>Master: Buffer all new write commands<br/>received from the clients
end
Note right of Master: Diskless replication
Master-->>Replica: RDB + buffered commands
end
Replica-)Master: Acknowledgement of data processed
Failure Detection
NODE_TIMEOUT
- Unresponsive master node is considered to be failing and can be replaced by one of its replicas
- If a master node cannot sense the majority of the other masters, it enters error state
Pub/sub
SUBSCRIBE, UNSUBSCRIBE and PUBLISH.
at-most-once message delivery semantics
Messages are sharded.
Redis Streams
Redis Sentinel
Provides high availability for Redis when not using Redis Cluster.
- Automatic failover: high availability
- Monitoring
- Notification
- Configuration provider
Redis + Sentinel as a whole are an eventually consistent system where the merge function is last failover wins.
---
title: Failover
---
sequenceDiagram
activate Master
Sentinel->>Master: PING
deactivate Master
Note right of Sentinel: No valid reply for down-after-milliseconds
Note right of Sentinel: SDOWN
loop Failure detection
Sentinel->>Sentinel: >= quorum
end
Note right of Sentinel: ODOWN
loop Vote
Sentinel->>Sentinel: >= max(majority, quorum)
end
Note right of Sentinel: Replica selection
Sentinel->>Elected Replica: REPLICAOF NO ONE
Elected Replica--)Sentinel: The switch is observed in INFO
loop Broadcasting
Sentinel->>Sentinel: Configuration (with epoch)
end
Sentinel->>Other Replicas: Reconfigure
activate Master
Sentinel->>Master: Reconfigure
deactivate Master
Memcached
Apache Kafka
Persistence
File system + Page cache
Persistent queue: simple reads and appends to files
- All operations are O(1)
- eads do not block writes or each other.
Servers
- Brokers
- Kafka Connect: continuously import and export data as event streams to integrate Kafka with your existing systems such as relational databases as well as other Kafka clusters.
Event: key, value, timestamp and ptional metadata headers
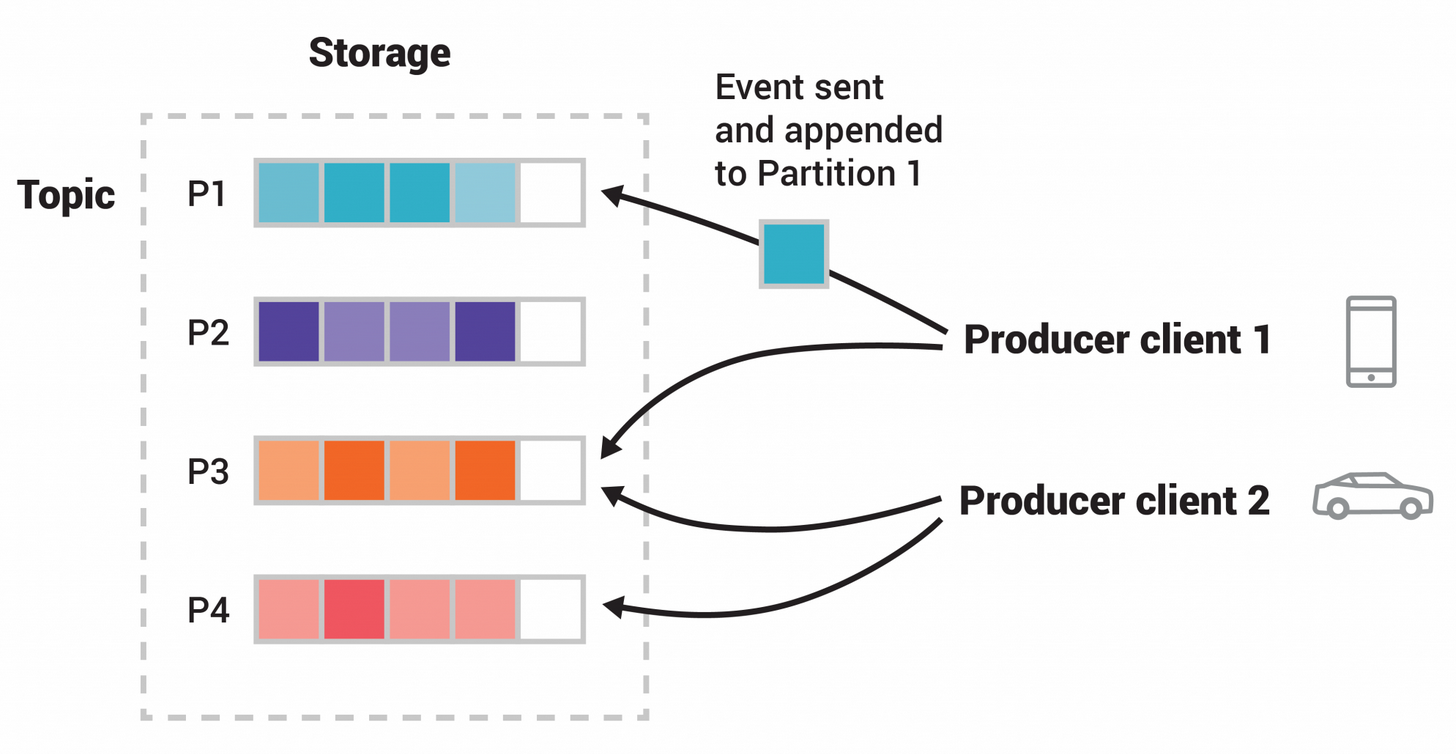
Topic
- Multi-publisher and multi-subscriber
- Event retain is configurable (not deleted after consumption)
- Partitioned
- Scalability
- Append-only sequence of records arranged chronologically
- Per partition read preserves order
- Replicated: RF = 3 by default
- Each record is given an offset
- A single topic can contain multiple partition logs (parallel processing)
- Topic’s default retention time: 7 days
Event -> File; Topic -> Folder
Replication
- A replica is the redundant element of a topic partition
- Each partition contains one or more replicas across brokers
- Each partition has Leader + Followers
- Per partition, “at least one” delivery semantics
- ISR: In-Sync Replica. A replica that has been out of ISR for a long period of time indicates that the follower is unable to fetch data at the same rate as the leader
- Geo-Replication: MirrorMaker
Brokers -> Cluster
- Managed by Kafka Raft (Kraft) Protocol
- Each broker handles GB (~10^5 count) R/W /s
- Broker leader election
- Stateless
- Multi-tenant: allow for many topics on the same cluster.
- Unbalanced cluster
- Leader skew. Solutions:
- auto.leader.rebalance.enable=true
- Kafka-preferred-replica-election.sh
- Broker skew. Solutions:
- Partition reassignment tool
- Leader skew. Solutions:
Producers
- Transmit JSON-format data to broker is in a compressed batch
- Batch size
- Liner duration
Consumers -> Consumer Group
- Pull model
- For a topic, #(customers) == #(partitions) to ensure consumers keep up with producers
Maximum message size: 1MB High throughput: millions of messages per second
- Fault-tolerant storage
- Pub/sub
- Monitor metrics/security logs
- Stream processing (inefficient for data transformations)
Kafka Schema Registry: ensures the (Avro) schema used by the consumer and the producer are identical. The producer submits the schema ID using the Confluent schema registry in Kafka.
- Log compaction
- For each topic partition, at least the last known value for each message key within the log of data is kept.
- Restoration
- Quotas
- Byte-rate limits that are set for each client-id
- Prevent a single application from monopolizing broker resources
Message Delivery Semantics
- At most once
- At least once
- Exactly once
RabbitMQ
Database
Amazon DynamoDB
Data Versioning
Vector clock
- (node, count)
- Clock truncation scheme
Handling Failures
Sloppy quorum: all read and write operations are performed on the first N healthy nodes from the preference list
---
title: Hinted Handoff
---
sequenceDiagram
Client->>Node A: Write
Note left of Node A: Node A is unavailable
Client->>Node B: Send replica
Node B->>Node B: Store a hint of the intended recipient <br/> (Node A) to metadata
Node B->>Node B Local Database: Store the hinted replica
Node B-) Node B Local Database: Scan periodically
Activate Node A
Note right of Node A: Node A is recovered
Node B->>Node A: Send replica
Node B-) Node B Local Database: Delete the replica
Deactivate Node A
Consistency
R, W and N
Apache Cassandra
PiB+
Column family: a container for an ordered collection of rows Row: an ordered collection of columns
- Row key
- Column keys
- Column values
Primary Key
- Single Primary Key
- Compound Primary Key
- Partitioning Key + Clustering Key
- Clustering is the process that sorts data in the partition
- Composite Partitioning Key
Data Partitioning (Dynamo Style)
LWW-Element-Set CRDT (Last-Write-Wins)
The default partitioner is the Murmur3Partitioner (MurmurHash)
Consistent Hashing
- vnode
- The more tokens, the higher the probability of an outage
- Cluster-wide maintenance operations are often slowed
- Performance of operations that span token rangs could be affected
Multi-Master Replication
Replication strategy
NetworkTopologyStrategy: requires a specifiedreplication_factor(RF) per datacenter; rack-aware (Snitch)SimpleStrategy: allows a single RF to be defined; only for testing clusters
Replica synchronization
- Best effort
- Read path: Read repair
- Monotonic Quorum Reads (
BLOCKING): in 2 successive quorum reads, it’s guaranteed the 2nd one won’t get something older than the 1st one - Write Atomicity (
NONE): prevents reading partially applied writes; partition level
- Monotonic Quorum Reads (
- Write path: Hinted handoff
- Read path: Read repair
- Anti-entropy repair: Full repair; compare hierarchical hash-trees across replicas using Merkle Tree
- Sub-range repair: increase the resolution of the hash trees
- Incremental: only repair the partitions that have changed since the last repair
Data Versioning
Mutation timestamp versioning: requires time synchronization (NTP.)
Consistency
Tunable:
ONETWOTHREEQUORUMALLLOCAL_QUORUMEACH_QUORUMLOCAL_ONEANY: a single replica may respond, or the coordinator may store a hint. Accepted for write operations only.
Operations:
- Write: always sent to all replicas, regardless of consistency level
- Read: sent to enough replicas to satisfy the consistency level
- One exception: when speculative retry may issue a redundant read request to an extra replica if the original replicas have not responded within a specified time window
Failure detection
Gossip Protocol
Cluster bootstrapping information
- State information: versioned with vector clock of (generation, version)
- Token metadata
- Schema version
Seed nodes
- Designated at cluster bootstrap
- Hotspots for gossip
Non-seed nodes
- Must contact at least one seed node to bootstrap into the cluster.
- Often contacts one seed node for each rack or datacenter.
Every node, every second:
- Updates the local node’s heartbeat state (the version) and constructs the node’s local view of the cluster gossip endpoint state.
- Picks a random other node in the cluster to exchange gossip endpoint state with.
- Probabilistically attempts to gossip with any unreachable nodes (if one exists)
- Gossips with a seed node if that didn’t happen in step 2.
Storage Engine
Log Structured Merge (LSM) Tree
- CommitLog: an append-only log of all mutations local to a node
- MemTables: in-memory structures where Cassandra buffers writes
- One active memtable per table
- SSTables: the immutable data files that Cassandra uses for persisting data on disk
- Cassandra triggers compactions which combine multiple SSTables into one
- Write: CommitLog -> MemTables -> SSTable
- Read: Bloom Filter -> Partition Key Cache -> Partition Index
MongoDB
Apache HBase
Wide column. Time series data
InfluxDB
Time series data
Distributed File System
Apache Hadoop File System (HDFS)
Availability Scalability Performance
CAP Theorem: Consistency, Availability and Parition Tolerance
Distributed cache:
- Dedicated cache cluster
- Co-located cache
Shards: consistent hashing (cache client, server (Redis) or cache proxy (Twemproxy))
Drawbacks:
- Domino effect
- Uneven server distribution
Solution:
- Add each server on the circle multiple times
- Jump Hash algorithm (Google)
- Proportional Hash (Yahoo!)
Possible problem: hot shard
Hot partition solution:
- Include event time to the parition key
- Split hot parition into more partitions
- Dedicated parition for popular items
Configuration management tool
- Chef
- Puppet
Configuration Service:
- Apache ZooKeeper
Data replication: availability Protocols:
- Probabilistic: gossip, epidemic broadcast tree, bimodal multicase
- Eventual consistency
- Consensus: 2 or 3 phase commit, Paxos, Raft, chain replication
- Strong consistency
Leader-Follower replication:
- Leader: put, get
- Follower: get (deals with hot shards problem)
Leader election:
- Configuration service (Apache ZooKeeper, Redis Sentinel)
- Implement in cluster
Data replication is asynchronous, which may cause failures or inconsistency
Source of inconsistency:
- Asynchronous data replication
- Inconsistent server list
Expired items:
- Passive expire: remove when read them
- Active expire: a thread runs periodically to clean. If dataset is too big, test a several items use probablistic algorithms at every run
Firwall to protect cache server ports Cache elements can be encrypted
Databases ca handle millions of requests per second (source?)
MapReduce
Distributed Coordination Service
- Synchronization
- Configuration maintenance
- Groups and naming
Apache ZooKeeper
Apache ZooKeeper: high performace, high availability, strictly ordered access.
- Shared hierarchical namespace (file system)
- Data registers - znodes (files and directories)
- Data are in-memory (high throughput, low latency)
- Ordered: stamps each update with a number that reflects the order of all transactions
- Single system image: a client’s view of the service keeps the same regardless of the server that it connects to
Znodes
- Coordination Data
- Each node can have data associated with it (like a file system that allows a file to also be a directory)
- Data stored at each znode is usually small (B ~ KB)
- R/W
- Atomic
- Works best for read-dominant workload: (r/w ratios = 10:1)
- Client
- Client maintains a TCP connection to a znode
- Client can set a watch which will be triggered and removed when the znode changes
- Persistent znodes
- Ephemeral znodes: live only when the session that created the znode is alive
- Sequential znodes: have a unique, monotonically increasing sequence number automatically appended to its name upon creation. Can be either persistent or ephemeral.
Znode stat structure
- Version numbers for data changes
- ACL changes
- Timestamps
Replication
Ensemble: a set of hosts
Servers must all know about each other
- In-memory: image of state
- Persistent storage: transaction logs and snapshots
ZooKeeper is available if a majority of the servers are available
Leader election: Sequential feature??
Leader-Follower
Client requests
- Read: serviced from the local replica of each server database
- Write: processed by an atomic agreement protocol
- All write requests from clients are forwarded to the leader
- The messaging layer takes care of replacing leaders on failures and syncing followers with leaders
- Local replicas never diverge
Others
Counter-based algorithms
- Count-min sketch
- Lossy counting
- Sapce saving
- Sticky sampling
Lambda Architecture Nathan Marz, Apache Storm, Jay Kreps, Apache Kafka
Stream Processing Framework
Apache Spark
Apache Flink
Front-end
- Request valiation
- Authentication/Authorization
- TLS termination
- Server-side encryption
- Caching
- Rate limiting
- Request dispatching
- Request deduplication
Usage data collection
- Users/Customers
- Who
- How
- Scale
- Requests per second
- Traffic spikes
- Performace
- Latency
- Cost
- Development cost
- Maintenance cost
SQL: Normalization Sharding, Cluster proxy (configuration service), shard proxy
- Cache
- Monitor health
- Publish metris
- Terminate long queries Vitess (YouTube)
SQL
- ACID transactions
- Complex dynamic queries
- Data analytics
- Data warehousing
NoSQL
- Easy scaling for both writes and reads
- Highly available
- Tolerate network partitions
Some keywords:
- Scalable: partitioning
- Reliable: replication and checkpointing
- Fast: in-memory
Data enrichment Embedded database (LinkedIn): RocksDB
Client
- blocking: create one thread for each new connection, easy to debug
- non-blocking I/O
Batching:
- increases throughput
- saves on cost
- request compression
Timeouts
- Connection timeout: tens of ms
- Request timeout: exponential backoff and jitter
- Circuite Breaker: prevents repeat retries
Resource dispatching
- Bulkhead pattern: isolates elements of an application into pools.
Load balancers
- Round robin
- Least connections
- Least response time
- Hash-based
Service discovery:
- Server-side: load balancer
- Client-side
- Service registry (e.g. Apache ZooKeeper, Netflix Eureka)
- Gossip protocol
Replication
- Single leader: SQL scaling
- Multi leader: (TBD)
- Leaderless: Apache Cassandra
Binary formats:
- Thrift: tag
- Protocol buffers: tag
- Avro
Storage strategy: Data rollup Hot/Cold storage Data federation
Clients:
- Netty: Non-blocking I/O
- Netflix Hystrix
- Polly
Load balancer:
- NetScaler: hardware
- NGINX: software
Performace testing
- Load testing
- Stress testing: find break point
- Soak testing: find leaking resources Apache JMeter to generate load
Monitoring:
- Latency
- Traffic
- Errors
- Saturation
Audit System:
- Weak: Canary
- Strong: Different path, Lambda Architecture
Queue message deletion:
- Offset (Apache Kafka)
- Mark as invisible so other cosumers won’t see it. The consumer who retrieved the message deletes it explicitly, otherwise it becomes visible again (AWS SQS)
Message delivery:
- At most once
- At least once
- Exactly once (hard to achieve)
Message sharing
- Broadcasting (full mesh)
- Gossip protocol (< several thousands)
- Redis
- Coordination service
Service + Daemon
maxmemory: write commands starts to fail or evict keys
Twitter Snowflake: Unique ID generator