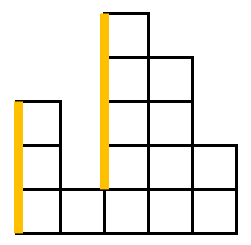
Subarray
Subarray
Definition
1
a[i], a[i + 1], ..., a[j]
Where 0 <= i <= j <= a.length
Algorithm
Minimum Moves to Make Array Complementary
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
public int minMoves(int[] nums, int limit) {
// delta array
// let target T = nums[i] + nums[n - 1 - i]
// changing T from (i - 1) to i takes p[i] more operations
// 2 <= T <= 2 * limit
int[] p = new int[2 * limit + 2];
// 2 1 0 1 2
// |----------|-----------|------------|----------------|
// 2 min(a, b) + 1 a + b max(a, b) + limit 2 * limit
//
int n = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++) {
int a = nums[i], b = nums[n - 1 - i];
p[2] += 2; // [2, min(a,b)]
p[Math.min(a, b) + 1]--; // (min(a, b), a + b)
p[a + b]--;
p[a + b + 1]++; // (a + b, max(a, b) + limit]
p[Math.max(a, b) + limit + 1]++; // (max(a, b) + limit, 2 * limit]
}
int move = 2 * n, sum = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= 2 * limit; i++) {
sum += p[i];
move = Math.min(move, sum);
}
return move;
}
Minimum Number of Increments on Subarrays to Form a Target Array
Credit to @coder206
e.g. [3,1,5,4,2]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public int minNumberOperations(int[] target) {
// count of exposed left edges
int count = target[0];
for (int i = 1; i < target.length; i++) {
count += Math.max(target[i] - target[i - 1], 0);
}
return count;
}
Two Pointers
Shortest Unsorted Continuous Subarray
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public int findUnsortedSubarray(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length, start = -1, end = -2, min = nums[n - 1], max = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, nums[i]);
min = Math.min(min, nums[n - 1 - i]);
// `end` is the rightmost index of an element which < the max of all the elements on its left
if (nums[i] < max) {
end = i;
}
// `start` is the leftmost index of an element which > the min of all the elements on its right
if (nums[n - 1 - i] > min) {
start = n - 1 - i;
}
// from the definitions of `start` and `end`:
// - all elements on the right of `end` > the max of all the elements on its left
// - all elements on the left of `start` < the min of all the elements on its right
// so these two parts are good
//
// `start` and `end` are not sorted by defintion, so the subarray bounds are tight
}
return end - start + 1;
}
Dynamic Programming
Find Two Non-overlapping Sub-arrays Each With Target Sum
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
private static final int MAX = (int)1e5 + 1;
public int minSumOfLengths(int[] arr, int target) {
int n = arr.length;
// dp[k]: minimum length of subarray arr[i...j]
// - sum(arr[i...j]) == target
// - 0 <= i <= j <= k
int[] dp = new int[n];
int i = 0, j = 0, sum = 0, result = MAX;
int minLen = MAX; // min length of required subarrays so far
while (j < n) {
// sliding window
// based on the fact that all integers are positive
// and target > 0
sum += arr[j];
while (sum > target) {
sum -= arr[i++];
}
if (sum == target) {
int currLen = j - i + 1; // length of the current required subarray
minLen = Math.min(minLen, currLen);
if (i > 0 && dp[i - 1] > 0) {
result = Math.min(result, dp[i - 1] + currLen);
}
}
dp[j++] = minLen;
}
return result == MAX ? -1 : result;
}
Generalization: k non-overlapping subarrays
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
private static final int MAX = (int)1e5 + 1;
private Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
public int minSumOfLengths(int[] arr, int target) {
return minSumOfLengths(arr, target, 2);
}
// k non-overlapping sub-arrays
private int minSumOfLengths(int[] arr, int target, int k) {
int n = arr.length;
// dp[t][m]: minimum sum of the lengths of m non-overlapping sub-arrays arr[i...j]
// - sum(arr[i...j]) == target
// - 0 <= i <= j < t
int[][] dp = new int[n + 1][k + 1]; //if asking for n subarrays, change 3 to n+1
map.put(0, 0);
// initialization
Arrays.fill(dp[0], MAX);
// length of 0 subarrays is 0
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i][0] = 0;
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sum += arr[i - 1];
map.put(sum, i);
// arr[d + 1 ... i] == target
int d = map.getOrDefault(sum - target, -1);
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
if (d >= 0) {
// len(arr[d + 1 ... i]) == i - d
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], dp[d][j - 1] + i - d);
}
}
}
return dp[n][k] == MAX ? -1 : dp[n][k];
}
Maximum Sum of 3 Non-Overlapping Subarrays
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
public int[] maxSumOfThreeSubarrays(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] p = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
p[i + 1] = p[i] + nums[i];
}
int[] left = new int[n], right = new int[n];
// starting position in left
// left[k] = 0
for (int i = k, max = p[k] - p[0]; i < n; i++) {
int start = i + 1 - k, sum = p[i + 1] - p[start];
// strict >
// because the result is the lexicographically smallest one
if (sum > max) {
left[i] = start;
max = sum;
} else {
left[i] = left[i - 1];
}
}
// starting position in right
right[n - k] = n - k;
for (int i = n - k - 1, max = p[n] - p[n - k]; i >= 0; i--) {
int start = i, sum = p[i + k] - p[start];
// non-strict >=
// because the result is the lexicographically smallest one
if (sum >= max) {
right[i] = start;
max = sum;
} else {
right[i] = right[i + 1];
}
}
int[] result = new int[3];
int max = 0;
// iterates all middle intervals
for (int i = k; i <= n - 2 * k; i++) {
int l = left[i - 1], r = right[i + k];
int sum = (p[i + k] - p[i]) + (p[l + k] - p[l]) + (p[r + k] - p[r]);
if (sum > max) {
max = sum;
result[0] = l;
result[1] = i;
result[2] = r;
}
}
return result;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public int numberOfnumsrithmeticSlices(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] dp = new int[n];
int count = 0;
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] - nums[i - 1] == nums[i - 1] - nums[i - 2]) {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 1;
count += dp[i];
}
}
return count;
}
Reduced to 0D:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public int numberOfArithmeticSlices(int[] nums) {
int dp = 0, count = 0;
for (int i = 2; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] - nums[i - 1] == nums[i - 1] - nums[i - 2]) {
dp++;
count += dp;
} else {
dp = 0;
}
}
return count;
}
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.