Iteration
Length of the Longest Valid Substring
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| private static final int MAX_FORBIDDEN_LEN = 10;
public int longestValidSubstring(String word, List<String> forbidden) {
Set<String> set = new HashSet(forbidden);
int max = 0, n = word.length(), i = n - 1, j = n;
while (i >= 0) {
// if word.substring(i + 1, j) is valid
// finds the longest k' where word.substring(i, k') is not forbidden
// then word.substring(i, k' + 1) is valid
for (int k = i; k < Math.min(i + MAX_FORBIDDEN_LEN, j); k++) {
if (set.contains(word.substring(i, k + 1))) {
j = k;
break;
}
}
max = Math.max(max, j - i--);
// now word.substring(i + 1, j) is valid
}
return max;
}
|
KMP
Knuth–Morris–Pratt (KMP) algorithm
LPS
- Construct an auxiliary array
lps[] of the same size as pattern lps[i] is the length of the longest matching proper prefix of the sub-pattern pat[0...i], which is also a suffix of the sub-pattern pat[0...i]. A proper prefix of a string is a prefix that is not equal to the string itself.
For example, for the pattern AABAACAABAA,
1
| lps[] = [0, 1, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| vector<int> computeLps(const string& s) {
int m = s.length();
vector<int> lps(m);
// lps[0] == 0
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i < m; i++) {
while (j > 0 && s[i] != s[j]) {
j = lps[j - 1];
}
if (s[i] == s[j]) {
lps[i] = ++j;
}
}
return lps;
}
|
Longest Happy Prefix
1
2
3
| public String longestPrefix(String s) {
return s.substring(0, computeLps(s)[s.length() - 1]);
}
|
Shortest Palindrome
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public String shortestPalindrome(String s) {
// "abace" -> "ec" + "aba" + "ce"
// Finds the longest prefix palindrome of s
int[] lps = computeLps(s + "#" + new StringBuilder(s).reverse().toString());
return new StringBuilder(s.substring(lps[lps.length - 1])).reverse().toString() + s;
}
|
Number of Subarrays That Match a Pattern II
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| int countMatchingSubarrays(vector<int>& nums, vector<int>& pattern) {
const int p = pattern.size();
// Delimiter
pattern.push_back(2);
for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {
pattern.push_back(nums[i - 1] < nums[i] ? 1 : nums[i - 1] == nums[i] ? 0 : -1);
}
vector<int> lps = computeLps(pattern);
return accumulate(lps.begin(), lps.end(), 0, [&](int a, int b) { return a + (b == p); });
}
|
Find Beautiful Indices in the Given Array II
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| void getIndices(string& s, string& a, vector<int>& v){
string t = a + "#" + s;
vector<int> lps = computeLps(t);
for (int i = 0; i < lps.size(); i++) {
if (lps[i] == a.length()) {
v.push_back(i - 2 * a.length());
}
}
}
|
Sum of Scores of Built Strings
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| long long sumScores(string s) {
vector<int> lps = computeLps(s);
int m = lps.size();
// dp[i]: how many non-zero j's there are such that s[j..i] is a prefix of the entire string s.
vector<int> dp(m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (int j = lps[i]; j) {
// Denotes the starting index of the longest command prefix ending at s[i] as k,
// then s[k...i] is a "shift" of s[0...(lps[i] - 1)].
// "+1" is s[0...(lps[i] - 1)] itself, since dp[lps[i] - 1] doesn't include s[0...(lps[i] - 1)].
//
// e.g. "bababba"
// lps: [0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2]
// dp: [0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1]
// ^
// dp[4] = 2
// s[4...4] = "b", s[2...4] = "bab"
// lps[4] = 3 = "bab"
// s[2...2] -> s[4...4] (dp[2])
// s[0...2] -> s[2...4] (longest common prefix ending at s[4]) ("+1")
dp[i] = dp[j - 1] + 1;
}
}
// The longest common prefix between s_i and s_n is denoted as s[n - i, j],
// where n - i <= j < n if the prefix exists.
// For any character k such that n - i <= k <= j, s[n - i, k] is counted in dp[k].
// So, sum(dp) is a superset of sum(score).
// Next, we prove sum(dp) is a subset of sum(score), therefore sum(dp) == sum(score).
// Without generality, we focus on any common prefix included in dp[i] as s[j...i].
// s[j...i] will either be the longest common prefix between s_(n - j) and s_n,
// or a prefix of that longest common prefix. So, it always contributes to sum(score).
return accumulate(dp.begin(), dp.end(), 0ll) + m;
}
|
More intuitively, Z-function is a better solution to this problem.
Maximum Deletions on a String
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| int deleteString(string s) {
int n = s.length();
vector<int> dp(n);
dp[n - 1] = 1;
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
dp[i] = 1;
vector<int> lps = computeLps(s.substr(i));
for (int j = 1; i + j < n; j += 2) {
// Uses LPS to quickly find a prefix which can be split to two identical parts
// e.g. "aaab", i = 0, j = 1
// lps[1] = 1, which means "aa" is a good prefix
if (lps[j] == j / 2 + 1) {
dp[i] = max(dp[i], 1 + dp[i + lps[j]]);
}
}
}
return dp[0];
}
|
Pattern Searching
- Search pattern in text with the help of
lps[]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| // finds the start indices of matches
List<Integer> kmp(String text, String pattern) {
int n = text.length(), m = pattern.length();
int[] lps = computeLps(pattern);
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (j == m || (j > 0 && pattern.charAt(j) != text.charAt(i))) {
j = lps[j - 1];
}
if (pattern.charAt(j) == text.charAt(i)) {
if (++j == m) {
list.add(i - j + 1);
}
}
}
return list;
}
|
Remove All Occurrences of a Substring
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| public String removeOccurrences(String s, String part) {
int n = s.length(), m = part.length();
int[] lps = computeLps(part);
Deque<Character> st = new ArrayDeque<>();
// stores pattern index j so that after character deletion it can be restored
int[] index = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; i++) {
st.push(s.charAt(i));
if (st.peek() == part.charAt(j)) {
// stores the next index of j
index[st.size()] = ++j;
if (j == m) {
// deletes the whole part when a match is found
int count = m;
while (count > 0) {
st.pop();
count--;
}
// restores the index of j to find next match
j = st.isEmpty() ? 0 : index[st.size()];
}
} else {
if (j > 0) {
j = lps[j - 1];
st.pop();
i--;
} else {
// resets the stored index
index[st.size()] = 0;
}
}
}
return new StringBuilder(st.stream().map(Object::toString).collect(Collectors.joining())).reverse().toString();
}
|
Find All Good Strings
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| private static final int MOD = (int)1e9 + 7;
private String s1, s2, evil;
private int[] memo = new int[1 << 17];
private int[] lps;
public int findGoodStrings(int n, String s1, String s2, String evil) {
this.s1 = s1;
this.s2 = s2;
this.evil = evil;
this.lps = computeLps(evil);
return dfs(0, 0, true, true);
}
// builds one character at each level
private int dfs(int index, int evilMatched, boolean startInclusive, boolean endInclusive) {
// KMP found a match of evil
// stops searching
if (evilMatched == evil.length()) {
return 0;
}
// built a good string
if (index == s1.length()) {
return 1;
}
int key = getKey(index, evilMatched, startInclusive, endInclusive);
if (memo[key] != 0) {
return memo[key];
}
int count = 0;
char from = startInclusive ? s1.charAt(index) : 'a';
char to = endInclusive ? s2.charAt(index) : 'z';
for (char c = from; c <= to; c++) {
// KMP to count the number of matches of pattern `evil` in current built text (path from root to c)
int j = evilMatched;
while (j > 0 && evil.charAt(j) != c) {
j = lps[j - 1];
}
if (c == evil.charAt(j)) {
j++;
}
count = (count + dfs(index + 1, j, startInclusive && (c == from), endInclusive && (c == to))) % MOD;
}
return memo[key] = count;
}
private int getKey(int n, int m, boolean b1, boolean b2) {
// 9 bits to store n (2 ^ 9 = 512)
// 6 bits to store m (2 ^ 6 = 64)
// 1 bit to store b1
// 1 bit to store b2
// 17 bits in total
return (n << 8) | (m << 2) | ((b1 ? 1 : 0) << 1) | (b2 ? 1 : 0);
}
|
For example, n = 2, s1 = "aa", s2 = "da", evil = "b"
Z-Function
Z-function and its calculation: z[i] is the length of the longest string that is, at the same time, a prefix of s and a prefix of s.substr(i).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| // O(n)
vector<int> computeZ(const string& s) {
int n = s.length();
vector<int> z(n);
for (int i = 1, l = 0, r = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i <= r) {
z[i] = min(r - i + 1, z[i - l]);
}
while (i + z[i] < n && s[z[i]] == s[i + z[i]]) {
z[i]++;
}
if (i + z[i] - 1 > r) {
l = i;
r = i + z[i] - 1;
}
}
return z;
}
|
Sum of Scores of Built Strings
1
2
3
| public long sumScores(String s) {
return Arrays.stream(computeZ(s)).asLongStream().sum() + s.length();
}
|
Minimum Time to Revert Word to Initial State II
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| int minimumTimeToInitialState(string word, int k) {
int res = 1, n = word.size();
auto z = computeZ(word);
while (k * res < n) {
if (z[k * res] >= n - k * res) {
break;
}
res++;
}
return res;
}
|
Rolling Hash
Longest Happy Prefix
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public String longestPrefix(String s) {
long h1 = 0, h2 = 0, mul = 1, mod = (long)1e9 + 7;
int len = 0;
for (int i = 0, j = s.length() - 1; j > 0; i++, j--) {
h1 = (h1 * 26 + s.charAt(i) - 'a') % mod;
h2 = (h2 + mul * (s.charAt(j) - 'a')) % mod;
mul = mul * 26 % mod;
if (h1 == h2) {
// compares the string every time you find a matching hash
// but only for characters we haven't checked before
if (s.substring(len, i + 1).compareTo(s.substring(j + len)) == 0) {
len = i + 1;
}
}
}
return s.substring(0, len);
}
|
Rabin-Karp algorithm: a string-searching algorithm that uses hashing to find an exact match of a pattern string in a text. It uses a rolling hash to quickly filter out positions of the text that cannot match the pattern, and then checks for a match at the remaining positions.
\[h(x) = \sum_{i = 0}^n a^{n - i}s_{i}\]
Longest Duplicate Substring
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
| // O(nlog(n))
public String longestDupSubstring(String s) {
// binary search
int low = 0, high = s.length() - 1;
while (low < high) {
int mid = low + (high - low + 1) / 2;
if (search(s, mid) != null) {
low = mid;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return search(s, low);
}
/**
* Searchs input string for duplicate substring with target length by Rabin-Karp Algorithm.
* @param s input string
* @param len target length
* @return duplicate substring with target length; null if not found
*/
private String search(String s, int len) {
if (len == 0) {
return "";
}
// polynomial rolling hash
long mod = (1 << 31) - 1, a = 256, h = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
h = (h * a + s.charAt(i)) % mod;
}
long coeff = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
coeff = (coeff * a) % mod;
}
// hash : start indexes
Map<Long, List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
// start index == 0
map.computeIfAbsent(h, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(0);
// start index > 0
int start = 0;
while (start + len < s.length()) {
// rolling hash
h = ((h + mod - coeff * s.charAt(start) % mod) * a + s.charAt(start + len)) % mod;
start++;
// Rabin-Karp collision check
map.putIfAbsent(h, new ArrayList<>());
for (int i : map.get(h)) {
if (s.substring(start, start + len).equals(s.substring(i, i + len))) {
return s.substring(i, i + len);
}
}
map.get(h).add(start);
}
// no duplicate substring found
return null;
}
|
Suffix Automaton
Suffix Automaton
Longest Common Subpath
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
| public class Solution {
public int longestCommonSubpath(int n, int[][] paths) {
// builds suffix automaton from the shortest path (denoted as path0)
return new SuffixAutomaton(Arrays.stream(paths).min(Comparator.comparingInt(p -> p.length)).get())
.longestCommonSubpath(paths);
}
// for a non-empty substring t of string s, endpos(t) is the set of all positions in the string s,
// in which the occurrences of t end
// e.g. s = "abcbc", endpos("bc") = {2, 4}
// endpos-equivalent substrings correspond to the same state
class State {
// len: length of the longest substring match of the state
// link: minLen(v) = len(link(v)) + 1
// link(v) represents a suffix of w, where w is the longest substring of state v
int len = 0, link = -1;
// next transitions
Map<Integer, Integer> next = new HashMap<>();
// lcs: longest common subpath (LCS) among all paths
int lcs;
}
class SuffixAutomaton {
private final State[] states;
private int size = 1, last = 0;
public SuffixAutomaton(int n) {
// the number of states of a string of length n doesn't exceed 2 * n - 1
this.states = new State[2 * n];
for (int i = 0; i < states.length; i++) {
states[i] = new State();
}
}
public SuffixAutomaton(int[] path) {
this(path.length);
build(path);
}
public void extend(int c) {
int curr = size++;
states[curr].len = states[last].len + 1;
int p = last;
// only adds a new transition of c if it doesn't exist already
while (p != -1 && !states[p].next.containsKey(c)) {
states[p].next.put(c, curr);
p = states[p].link;
}
if (p == -1) {
states[curr].link = 0;
} else {
int q = states[p].next.get(c);
if (states[p].len + 1 == states[q].len) {
// (p, q) is continuous
states[curr].link = q;
} else {
// splits q into two substates
int clone = size++;
states[clone].len = states[p].len + 1;
states[clone].next = new HashMap<>(states[q].next);
states[clone].link = states[q].link;
while (p != -1 && states[p].next.replace(c, q, clone)) {
p = states[p].link;
}
states[q].link = states[curr].link = clone;
}
}
last = curr;
}
// O(n * log(k))
public void build(int[] path) {
for (int c : path) {
extend(c);
}
// LCS is the longest substring match for the first (shortest) path
for (State s : states) {
s.lcs = s.len;
}
}
// calculates the LCS of each state
private void lcs(int[] path) {
// lcs[i]: LCS ending at state i
int[] lcs = new int[size];
// state and len of the current matching part
int p = 0, len = 0;
// for each position in `path`, finds the lcs of `path` and path0 ending in that position
for (int c : path) {
// shortens the current matching part
while (states[p].link >= 0 && !states[p].next.containsKey(c)) {
p = states[p].link;
len = states[p].len;
}
if (states[p].next.containsKey(c)) {
p = states[p].next.get(c);
lcs[p] = Math.max(lcs[p], ++len);
// traverses by suffix links to backfill all states with LCS's
// each state on the traversal is a suffix of longest substring matching of p
int q = states[p].link;
while (lcs[q] < states[q].len) {
lcs[q] = states[q].len;
q = states[q].link;
}
}
}
// state[i].lcs is the min among LCS of all paths at the state
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
states[i].lcs = Math.min(states[i].lcs, lcs[i]);
}
}
public int longestCommonSubpath(int[][] paths) {
for (int[] p : paths) {
lcs(p);
}
// finds the max LCS among all states
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, states[i].lcs);
}
return max;
}
}
}
|
Suffix Tree
Suffix Tree
Ukkonen’s Algorithm: time complexity of tree construction: \(O(nlog(k))\)
String Matching in an Array
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| public List<String> stringMatching(String[] words) {
TrieNode root = new TrieNode();
for (String w : words) {
for (int i = 0; i < w.length(); i++) {
insert(root, w.substring(i));
}
}
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (String w : words) {
TrieNode node = root;
for (char ch : w.toCharArray()) {
node = node.children[ch - 'a'];
}
if (node.count > 1) {
list.add(w);
}
}
return list;
}
class TrieNode {
TrieNode[] children = new TrieNode[26];
int count = 0;
}
private void insert(TrieNode root, String word) {
TrieNode node = root;
for (char ch : word.toCharArray()) {
if (node.children[ch - 'a'] == null) {
node.children[ch - 'a'] = new TrieNode();
}
node = node.children[ch - 'a'];
// increases the counter of all nodes on the path
// because we will search for "substring" instead of "suffix" in the trie,
// we can't only mark the last node
node.count++;
}
}
|
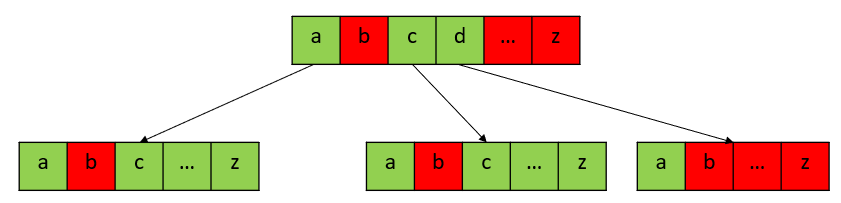
Trie
Count Prefix and Suffix Pairs II
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| truct TrieNode {
// key = s[i] * 128 + s[n - 1 - i]
unordered_map<int, TrieNode*> children;
// count of words that end at this node
int count = 0;
};
public:
long long countPrefixSuffixPairs(vector<string>& words) {
TrieNode* root = new TrieNode();
long long cnt = 0;
for (const string& w : words) {
TrieNode* itr = root;
for (int i = 0, n = w.size(); i < n; i++) {
auto& child = itr->children.emplace(w[i] * 128 + w[n - 1 - i], nullptr).first->second;
if (!child) {
child = new TrieNode();
}
itr = child;
// Include all words that share a common prefix and suffix with 'w' up to this point.
// The unique key construction ensures that only words with matching prefixes and suffixes
// at corresponding positions are counted.
cnt += itr->count;
}
itr->count++;
}
return cnt;
}
|