Scheduling
Greedy
Minimum Swaps to Make Strings Equal
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
public int minimumSwap(String s1, String s2) {
int[] count = new int[2];
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); i++) {
// ignores matched positions
if (s1.charAt(i) != s2.charAt(i)) {
count[s1.charAt(i) - 'x']++;
}
}
// case 3: "x" "y"
if ((count[0] + count[1]) % 2 == 1) {
return -1;
}
// count[0] % 2 == count[1] % 2
// case1: "xx" "yy" - 1 swap, apply as much as possible
// case2: "xy" "yx" - 2 swaps
return count[0] / 2 + count[1] / 2 + count[0] % 2 * 2;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public String longestDiverseString(int a, int b, int c) {
return helper(a, b, c, "a", "b", "c");
}
private String helper(int a, int b, int c, String sa, String sb, String sc) {
// preprocess, so that a >= b >= c
if (a < b) {
return helper(b, a, c, sb, sa, sc);
}
if (b < c) {
return helper(a, c, b, sa, sc, sb);
}
if (b == 0) {
return sa.repeat(Math.min(a, 2));
}
// greedy
int aUsed = Math.min(a, 2), bUsed = a - aUsed >= b ? 1 : 0;
return sa.repeat(aUsed) + sb.repeat(bUsed) + helper(a - aUsed, b - bUsed, c, sa, sb, sc);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
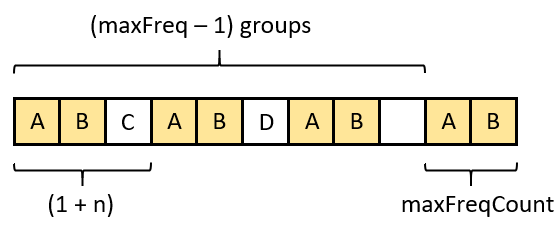
int leastInterval(vector<char>& tasks, int n) {
vector<int> freqs(26);
int maxFreq = 0, maxFreqCount = 0; // Count of the most frequent tasks
for (const char& ch : tasks) {
freqs[ch - 'A']++;
if (maxFreq == freqs[ch - 'A']) {
maxFreqCount++;
} else if (maxFreq < freqs[ch - 'A']) {
maxFreq = freqs[ch - 'A'];
maxFreqCount = 1;
}
}
// No idle vs has idle
return max(static_cast<int>(tasks.size()), (maxFreq - 1) * (n + 1) + maxFreqCount);
}
Maximum Number of Weeks for Which You Can Work
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
public long numberOfWeeks(int[] milestones) {
long sum = 0;
int max = 0;
for (int m : milestones) {
sum += m;
max = Math.max(max, m);
}
// Case 1: there are more than one max.
// takes turns working on projects that have max milestones
// e.g. [4, 4, 2, 1]
// -> [3, 3, 2, 1] +2
// -> [2, 2, 2, 1] +2
// -> [1, 1, 1, 1] +3
// -> [0, 0, 0, 0] +4
// Case 2: there is only one max
// strategy:
// - max: a0, second: a1, remaining projects: r
// 1. works on a0 and any one from r, until a0 is reduced to a1
// 2. then we have two max projects (a1) - back to Case 1
//
// for Step 1, it's required sum(r) >= a0 - a1
// -> sum(r) + a1 - a0 >= 0
// -> sum - 2 * max >= 0
// Case 3: the requirement in Step 1, Case 2 is not met
// stragy:
// max -> any one from others -> max -> ...
// e.g. [3, 1]
// -> [2, 0] +2
// -> [1, 0] +1
return (sum - max) < max ? 2 * (sum - max) + 1 : sum;
}
EDF
Earliest deadline first scheduling
Rearrange String k Distance Apart
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
public String rearrangeString(String s, int k) {
if (k == 0) {
return s;
}
int[] count = new int[26];
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
count[c - 'a']++;
}
Queue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(i -> -count[i]));
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (count[i] > 0) {
pq.offer(i);
}
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
// picks the char with highest frequency
int node = pq.poll();
sb.append((char)(node + 'a'));
count[node]--;
// adds used char to the queue
q.offer(node);
// maintains fixed size k
if (q.size() == k) {
// front char is already at least k char apart
int front = q.poll();
if (count[front] > 0) {
pq.offer(front);
}
}
}
return sb.length() == s.length() ? sb.toString() : "";
}
NP-Complete
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
// NP-complete
// O(3 ^ n)
public int minNumberOfSemesters(int n, int[][] dependencies, int k) {
// bit mask of prerequisite courses
int[] p = new int[n];
for (int[] d : dependencies) {
p[d[1] - 1] |= 1 << (d[0] - 1);
}
int[] dp = new int[1 << n];
Arrays.fill(dp, n);
dp[0] = 0;
// state represents the courses that have been taken so far
for (int state = 0; state < (1 << n); state++) {
int courses = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// prerequisite courses of i is a subset of current state
// so we can take course i
if ((state & p[i]) == p[i]) {
courses |= (1 << i);
}
}
// removes courses that have been taken
courses &= ~state;
// enumerates all subsets of courses
for (int s = courses; s > 0; s = (s - 1) & courses) {
if (Integer.bitCount(s) <= k) {
// state | s is the next state after taking the courses in s
dp[state | s] = Math.min(dp[state | s], dp[state] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[(1 << n) - 1];
}
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.