Random
Shuffle
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
private int[] arr;
private int[] oldArr;
private Random rand = new Random();
public Solution(int[] nums) {
arr = nums;
oldArr = nums.clone();
}
/** Resets the array to its original configuration and return it. */
public int[] reset() {
return oldArr;
}
/** Returns a random shuffling of the array. */
public int[] shuffle() {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
swap(i, i + rand.nextInt(arr.length - i));
}
return arr;
}
private void swap(int i, int j) {
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = tmp;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
private Map<Integer, Integer> map; // index : real index
private Random rand;
private int rows, cols, count;
public Solution(int n_rows, int n_cols) {
map = new HashMap<>();
rand = new Random();
rows = n_rows;
cols = n_cols;
reset();
}
public int[] flip() {
int index = rand.nextInt(count--);
// swaps the real index at index and count
int tmp = map.getOrDefault(index, index);
map.put(index, map.getOrDefault(count, count));
map.put(count, tmp);
return new int[]{tmp / cols, tmp % cols};
}
public void reset() {
// no need to clear the map
count = rows * cols;
}
Remapping
Map + List
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
private Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
private Random rand = new Random();
private int whitelistSize; // number of integers in whitelist
public Solution(int n, int[] blacklist) {
whitelistSize = n - blacklist.length;
// some blacklist integers already occupies positions in [whitelistSize, n)
for (int b : blacklist) {
if (b >= whitelistSize) {
map.put(b, -1);
}
}
// re-maps blacklist integers to the segment [whitelistSize, n)
int index = n - 1;
for (int b : blacklist) {
// finds the first vacant position in [whitelistSize, n)
// and maps b to it
if (b < whitelistSize) {
while (map.containsKey(index--)) {
}
map.put(b, index + 1);
}
}
}
public int pick() {
int num = rand.nextInt(whitelistSize);
return map.getOrDefault(num, num);
}
The above problem can be solved by binary search, too. But the time complexity will be higher:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
private int[] blacklist;
private Random rand = new Random();
private int whitelistSize; // number of integers in whitelist
public Solution(int n, int[] blacklist) {
this.blacklist = blacklist;
this.whitelistSize = n - blacklist.length;
Arrays.sort(blacklist);
}
// O(log(n))
public int pick() {
int num = rand.nextInt(whitelistSize);
// if num is in [0, blacklist[0]), returns num
// if num is in [blacklist[0], blacklist[1] - 1), returns num + 1
// ...
// if num is in [blacklist[i] - i, blacklist[i + 1] - (i + 1)), returns num + (i + 1)
// ...
// searches for the index of the first right boundary so that blacklist[index] - index > num
// i.e. blacklist[index] - index - 1 >= num
int low = 0, high = blacklist.length;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
if (blacklist[mid] - mid - 1 >= num) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return num + low;
}
Cumulative Probability
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
private int[] p; // cumulative sum
private Random rand = new Random();
public Solution(int[] w) {
p = new int[w.length + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < w.length; i++) {
p[i + 1] = p[i] + w[i];
}
}
public int pickIndex() {
// target range: [1, sum]
int index = Arrays.binarySearch(p, rand.nextInt(p[p.length - 1]) + 1);
// w starts from p[1], therefore index - 1
return (index < 0 ? ~index : index) - 1;
}
Multi-dimension
Random Point in Non-overlapping Rectangles
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
private int[][] rects;
private int[] p;
private Random rand = new Random();
public Solution(int[][] rects) {
this.rects = rects;
p = new int[rects.length + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < rects.length; i++) {
// number of points
p[i + 1] = p[i] + (rects[i][2] - rects[i][0] + 1) * (rects[i][3] - rects[i][1] + 1);
}
}
public int[] pick() {
int points = rand.nextInt(p[p.length - 1]) + 1;
int i = Arrays.binarySearch(p, points);
int index = i < 0 ? ~i : i;
// rect starts from p[1], therefore index - 1
int[] rect = rects[index - 1];
int left = rect[0], bottom = rect[1], right = rect[2], top = rect[3];
int x = left + (p[index] - points) % (right - left + 1);
int y = bottom + (p[index] - points) / (right - left + 1);
return new int[]{x, y};
}
Sampling
Rejection Sampling
Rejection sampling: acceptance-rejection method
The algorithm to obtain a sample from distribution \(X\) with density \(f\) using samples from distribution \(Y\) with density \(g\) is as follows:
- Obtain a sample \(y\) from distribution \(Y\) and a sample \(u\) from \(\mathrm {Unif} (0,1)\) (the uniform distribution over the unit interval).
- Check whether or not \(u<f(y)/Mg(y)\).
- If this holds, accept \(y\) as a sample drawn from \(f\);
- if not, reject the value of \(y\) and return to the sampling step.
The algorithm will take an average of \(M\) iterations to obtain a sample.
(from https://theclevermachine.files.wordpress.com/2012/09/rejectionsamplingcriterion.png?w=584)
Implement Rand10() Using Rand7()
(from https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-rand10-using-rand7/Figures/470/rejectionSamplingTable.png)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public int rand10() {
int row, col, index;
do {
row = rand7();
col = rand7();
index = col + (row - 1) * 7;
} while (index > 40);
return 1 + index % 10;
}
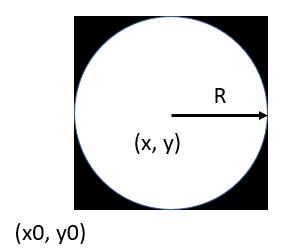
Generate Random Point in a Circle
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
private double r, x, y;
public Solution(double radius, double x_center, double y_center) {
this.r = radius;
this.x = x_center;
this.y = y_center;
}
public double[] randPoint() {
double x0 = x - r;
double y0 = y - r;
while (true) {
double xr = x0 + Math.random() * r * 2;
double yr = y0 + Math.random() * r * 2;
if ((xr - x) * (xr - x) + (yr - y) * (yr - y) <= r * r) {
return new double[]{xr, yr};
}
}
}
Inverse Transform Sampling
- Generate a random number \(u\) from the standard uniform distribution in the interval \([0,1]\), e.g. from \(U\sim \mathrm {Unif} [0,1]\)
- Find the inverse of the desired CDF, e.g. \(F_{X}^{-1}(x)\)
- Compute \(X=F_{X}^{-1}(u)\). The computed random variable \(X\) has distribution \(F_X(x)\)
Generate Random Point in a Circle
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
private double r, x, y;
public Solution(double radius, double x_center, double y_center) {
this.r = radius;
this.x = x_center;
this.y = y_center;
}
public double[] randPoint() {
// PDF: f(x) = 2 * r, R = 1
// CDF: F(x) = r ^ 2
// F' = sqrt(r)
double d = r * Math.sqrt(Math.random());
double theta = 2 * Math.random() * Math.PI;
return new double[]{x + d * Math.cos(theta), y + d * Math.sin(theta)};
}
Reservoir Sampling
Choosing a simple random sample, without replacement, of k items from a population of unknown size n in a single pass over the items.
Algorithm R:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
/**
* Reservoir sampling with Algorithm R.
* @param nums input array
* @param k reservoir size
* @return output reservoir array with randomly chosen items
*/
public int[] reservoirSample(int[] nums, int k) {
// fills the reservoir array
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
r[i] = nums[i];
}
// replaces elements with gradually decreasing probability
for (int i = k; i < nums.length; i++) {
int j = rand.nextInt(i + 1);
if (j < k) {
r[j] = nums[i];
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
private int[] nums;
private Random rand;
public Solution(int[] nums) {
this.nums = nums;
this.rand = new Random();
}
public int pick(int target) {
int index = -1, count = 0;
// reservoir size == 1
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] == target && rand.nextInt(++count) == 0) {
index = i;
}
}
return index;
}
Online Majority Element In Subarray
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
private Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
private int[] arr;
private Random rand = new Random();
public MajorityChecker(int[] arr) {
this.arr = arr;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
map.computeIfAbsent(arr[i], k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(i);
}
}
// gets the number of occurrences of the given element in the range
private int getOccurrence(int left, int right, int a) {
List<Integer> list = map.get(a);
int i = Collections.binarySearch(list, left);
if (i < 0) {
i = ~i;
}
if (i == list.size()) {
return 0;
}
int j = Collections.binarySearch(list, right);
if (j < 0) {
j = ~j - 1;
}
return j - i + 1;
}
private int getRandomNum(int l, int r) {
return rand.nextInt(r - l + 1) + l;
}
public int query(int left, int right, int threshold) {
// randomly picks an element in the range
// attempts 10 times
// probability of false negative < 0.5 ^ 20 ~= 1e-6
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int a = arr[getRandomNum(left, right)];
if (getOccurrence(left, right, a) >= threshold) {
return a;
}
}
return -1;
}