Multi-dimension
Search
Reduce to One-dimension
Monotonic in Each Dimenstion
Find Positive Integer Solution for a Given Equation
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public List<List<Integer>> findSolution(CustomFunction customfunction, int z) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
// starts from bottom-right
int x = 1, y = 1000;
while (x <= 1000 && y > 0) {
int v = customfunction.f(x, y);
if (v < z) {
x++;
} else if (v > z) {
y--;
} else {
result.add(Arrays.asList(x++, y--));
}
}
return result;
}
Dimension Reduction
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
int n1 = word1.length(), n2 = word2.length();
int[][] dp = new int[n1 + 1][n2 + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n1; i++) {
dp[i][0] = i;
}
for (int j = 1; j <= n2; j++) {
dp[0][j] = j;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n2; j++) {
if (word1.charAt(i - 1) == word2.charAt(j - 1)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][j - 1], Math.min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1])) + 1;
}
}
}
return dp[n1][n2];
}
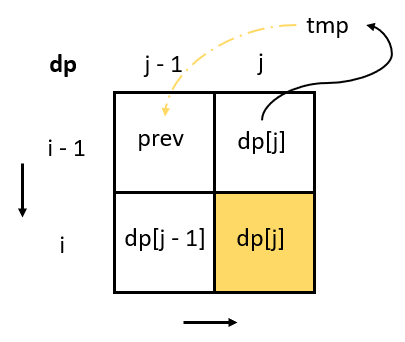
Rolling array optimization:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
int prev = 0, n1 = word1.length(), n2 = word2.length();
int[] dp = new int[word2.length() + 1];
for (int j = 1; j <= n2; j++) {
dp[j] = j;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n1; i++) {
prev = dp[0];
dp[0] = i;
for (int j = 1; j <= n2; j++) {
int tmp = dp[j];
if (word1.charAt(i - 1) == word2.charAt(j - 1)) {
dp[j] = prev;
} else {
dp[j] = Math.min(prev, Math.min(dp[j], dp[j - 1])) + 1;
}
prev = tmp;
}
}
return dp[n2];
}
Disconnect Path in a Binary Matrix by at Most One Flip
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
public boolean isPossibleToCutPath(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
// rolling DP
boolean[] dp = new boolean[n + 1];
dp[1] = true;
// openings[i]: number of reachable cells (openings) on the i-th anti-diagonal
int[] openings = new int[m + n - 1];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// checks if (i, j) is reachable from (0, 0)
dp[j + 1] = grid[i][j] == 1 && (dp[j + 1] || dp[j]);
openings[i + j] += dp[j + 1] ? 1 : 0;
}
}
// checks path count on each anti-diagnol layer
for (int i = 1; i < openings.length - 1; i++) {
if (openings[i] < 2) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
Projection
Smallest Rectangle Enclosing Black Pixels
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
public int minArea(char[][] image, int x, int y) {
int m = image.length, n = image[0].length;
// there's only one black region,
// so the horizontal/vertical projection is continuous
// horizontal projection
// first column that has black pixels
int left = binarySearch(image, 0, y, 0, m, true, true);
// first column that has all white pixels
int right = binarySearch(image, y, n, 0, m, false, true);
// vertical projection
// first row that has black pixels
int top = binarySearch(image, 0, x, left, right, true, false);
// first row that has all white pixels
int bottom = binarySearch(image, x, m, left, right, false, false);
return (right - left) * (bottom - top);
}
private int binarySearch(char[][] image, int low, int high, int min, int max, boolean isLowerBound, boolean isHorizontal) {
while (low < high) {
// k is the index of the first row/column which has black pixels
int k = min, mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
while (k < max && (isHorizontal ? image[k][mid] : image[mid][k]) == '0') {
k++;
}
if (k < max == isLowerBound) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return low;
}
Range Sum
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public int[][] matrixBlockSum(int[][] mat, int K) {
int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length;
int[][] rangeSum = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
// similar to prefix sum
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
rangeSum[i + 1][j + 1] = rangeSum[i + 1][j] + rangeSum[i][j + 1] - rangeSum[i][j] + mat[i][j];
}
}
int[][] sum = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int r1 = Math.max(0, i - K), c1 = Math.max(0, j - K), r2 = Math.min(m, i + K + 1), c2 = Math.min(n, j + K + 1);
sum[i][j] = rangeSum[r2][c2] - rangeSum[r2][c1] - rangeSum[r1][c2] + rangeSum[r1][c1];
}
}
return sum;
}
Maximum Side Length of a Square with Sum Less than or Equal to Threshold
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
public int maxSideLength(int[][] mat, int threshold) {
int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length;
int[][] p = new int[m + 1][n + 1]; // prefix sum
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
p[i + 1][j + 1] = p[i + 1][j] + p[i][j + 1] - p[i][j] + mat[i][j];
if (i - max >= 0 && j - max >= 0 && squareSum(p, i, j, max + 1) <= threshold) {
max++;
}
}
}
return max;
}
private int squareSum(int[][] p, int i, int j, int k) {
return p[i + 1][j + 1] - p[i + 1][j + 1 - k] - p[i + 1 - k][j + 1] + p[i + 1 - k][j + 1 - k];
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
public boolean possibleToStamp(int[][] grid, int stampHeight, int stampWidth) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
// stamp[i][j]: whether it's possible to fit the bottom right corner of a stamp at (i, j)
int[][] stamp = new int[m][n], p = initRangeSum(grid);
for (int i = stampHeight - 1; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = stampWidth - 1; j < n; j++) {
stamp[i][j] = sum(p, i - stampHeight + 1, j - stampWidth + 1, i, j) == 0 ? 1 : 0;
}
}
// grid[i][j] is covered by some stamp
// if there is a stamp with right bottom corner within the range (i, j) - (i + h - 1, j + w - 1)
p = initRangeSum(stamp);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 0 &&
sum(p, i, j, Math.min(m - 1, i + stampHeight - 1), Math.min(n - 1, j + stampWidth - 1)) == 0) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
private int[][] initRangeSum(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int[][] p = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
p[i + 1][j + 1] = p[i + 1][j] + p[i][j + 1] - p[i][j] + matrix[i][j];
}
}
return p;
}
private int sum(int[][] p, int r1, int c1, int r2, int c2) {
return p[r2 + 1][c2 + 1] - p[r2 + 1][c1] - p[r1][c2 + 1] + p[r1][c1];
}
2D Prefix Sum
2D -> 1D: Calculates prefix sum for each row, and then each column, or vice versa.
Number of Submatrices That Sum to Target
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
int[][] p = new int[m + 1][n];
// calculates prefix sum for each column
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
p[i + 1][j] = p[i][j] + matrix[i][j];
}
}
// rows in range [r1, r2]
for (int r1 = 0; r1 < m; r1++) {
for (int r2 = r1; r2 < m; r2++) {
// 560. Subarray Sum Equals K
count += subarraySum(p, r1, r2, target);
}
}
Alternatively,
1
2
3
4
5
6
// calculates prefix sum for row
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
p[i][j + 1] = p[i][j] + matrix[i][j];
}
}
Count
Stick to one orientation so the final result won’t duplicate.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public long[] countBlackBlocks(int m, int n, int[][] coordinates) {
Map<List<Integer>, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (var c : coordinates) {
incrementVal(map, c[0], c[1]);
incrementVal(map, c[0] - 1, c[1]);
incrementVal(map, c[0], c[1] - 1);
incrementVal(map, c[0] - 1, c[1] - 1);
}
long[] arr = new long[5];
for (var e : map.entrySet()) {
var k = e.getKey();
int r = k.get(0), c = k.get(1);
if (r >= 0 && r < m - 1 && c >= 0 && c < n - 1) {
arr[e.getValue()]++;
}
}
long sum = Arrays.stream(arr).sum();
arr[0] = ((long)m - 1) * (n - 1) - sum;
return arr;
}
private void incrementVal(Map<List<Integer>, Integer> map, int r, int c) {
var k = Arrays.asList(r, c);
map.put(k, map.getOrDefault(k, 0) + 1);
}
Traversal
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public int[] findDiagonalOrder(List<List<Integer>> nums) {
List<Deque<Integer>> diags = new ArrayList<>();
int n = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
List<Integer> row = nums.get(i);
for (int j = 0; j < row.size(); j++, n++) {
if (i + j == diags.size()) {
diags.add(new ArrayDeque<>());
}
diags.get(i + j).push(row.get(j));
}
}
int[] result = new int[n];
int i = 0;
for (Deque<Integer> d : diags) {
for (int num : d) {
result[i++] = num;
}
}
return result;
}
Flood Fill
Flood fill: also called seed fill, is an algorithm that determines and alters the area connected to a given node in a multi-dimensional array with some matching attribute.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
private static final int[][] DIRECTIONS = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
private int[][] grid;
private int m, n;
public int numEnclaves(int[][] grid) {
this.grid = grid;
this.m = grid.length;
this.n = grid[0].length;
// flood-fills the land (1 -> 0) from the boundary
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// boundary
if (i == 0 || j == 0 || i == m - 1 || j == n - 1) {
fill(i, j);
}
}
}
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
count += grid[i][j];
}
}
return count;
}
private void fill(int i, int j) {
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i == m || j == n || grid[i][j] == 0) {
return;
}
grid[i][j] = 0;
for (int[] d : DIRECTIONS) {
fill(i + d[0], j + d[1]);
}
}
Regular DFS/BFS would also work.
Sort
Largest Submatrix With Rearrangements
Swap
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
public int movesToChessboard(int[][] board) {
int n = board.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// two types of rows if it can transform to a chessboard
// e.g. if there's a row 01010011
// then any other row must be either 01010011 or 10101100 (inverse)
//
// corollary: the 4 corners of any rectangle inside the board must be one of the following:
// - 4 zeros
// - 2 zeros 2 ones
// - 4 ones
//
// checks the top left corner rectangle
if ((board[0][0] ^ board[i][0] ^ board[0][j] ^ board[i][j]) == 1) {
return -1;
}
}
}
// first row and column
// sum, i.e. count of ones
int rowSum = 0, colSum = 0;
// count of misplaced elements if the final pattern is "1010..."
// then the count of misplaced elements of inverse pattern ("0101...") is (n - misplaced)
int rowMisplaced = 0, colMisplaced = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
rowSum += board[0][i];
colSum += board[i][0];
if (board[i][0] == i % 2) {
rowMisplaced++;
}
if (board[0][i] == i % 2) {
colMisplaced++ ;
}
}
// - if n == 2 * k, then count(0) == count(1) == k
// - if n == 2 * k + 1, then count(0) == k, count(1) == k + 1
// or count(0) == k + 1, count(1) == k
//
// checking the first row and column is sufficient,
// because the top left corner rectangle is verified
if (rowSum != n / 2 && rowSum != (n + 1) / 2) {
return -1;
}
if (colSum != n / 2 && colSum != (n + 1) / 2) {
return -1;
}
if (n % 2 == 1) {
// when n is odd, only one final pattern is possible
//
// if misplaced is even, then the final pattern is "1010..."
// else the final pattern is the inverse ("0101...")
//
// e.g. n is odd, "001", misplaced == 1
// the final pattern should be the inverse "010",
// and the actual count of misplaced elements is 2 == n - misplaced
//
// in either case, the actual count of misplaced elements is even
if (colMisplaced % 2 == 1) {
colMisplaced = n - colMisplaced;
}
if (rowMisplaced % 2 == 1) {
rowMisplaced = n - rowMisplaced;
}
} else {
// when n is even
// the final pattern can be either "1010..." or the inverse "0101..."
//
// misplaced and (n - misplaced) are both even
// picks the minimum of them
colMisplaced = Math.min(n - colMisplaced, colMisplaced);
rowMisplaced = Math.min(n - rowMisplaced, rowMisplaced);
}
// one swap fixes two misplaced elements
return (colMisplaced + rowMisplaced) / 2;
}
Flip
Remove All Ones With Row and Column Flips
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public boolean removeOnes(int[][] grid) {
// order of flips doesn't matter
// e.g. r1 -> c1 is equivalant to c1 -> r1
// therefore we can flip all rows, then all colums
// checks if the current row is the same or the inverse of the first row
// e.g. 0101 vs 0101 vs 1010
// in this way, after flipping all rows,
// all columns are either all 1's or all 0's
for (int i = 1; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
if ((grid[i][j] ^ grid[0][j]) != (grid[i][0] ^ grid[0][0])) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
Linear Transformation
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
public int largestOverlap(int[][] img1, int[][] img2) {
int n = img1.length;
int count = 0;
// linear transformation
int[][] vectors = new int[2 * n][2 * n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// focuses on cells with ones
if (img1[i][j] == 0) {
continue;
}
for (int r = 0; r < n; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < n; c++) {
// focuses on cells with ones
if (img2[r][c] == 1) {
count = Math.max(count, ++vectors[n + i - r][n + j - c]);
}
}
}
}
}
return count;
}
Greedy
Find Valid Matrix Given Row and Column Sums
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public int[][] restoreMatrix(int[] rowSum, int[] colSum) {
int m = rowSum.length, n = colSum.length;
int[][] matrix = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
matrix[i][j] = Math.min(rowSum[i], colSum[j]);
rowSum[i] -= matrix[i][j];
colSum[j] -= matrix[i][j];
}
}
return matrix;
}