Sort
Sort List
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
| public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode();
dummy.next = head;
int n = 0;
while (head != null) {
head = head.next;
n++;
}
for (int step = 1; step < n; step <<= 1) {
ListNode prev = dummy, curr = dummy.next;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode left = curr, right = split(left, step);
curr = split(right, step);
prev = merge(left, right, prev);
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
private ListNode split(ListNode head, int step) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
for (int i = 1; head.next != null && i < step; i++) {
head = head.next;
}
ListNode right = head.next;
head.next = null;
return right;
}
private ListNode merge(ListNode left, ListNode right, ListNode prev) {
ListNode curr = prev;
while (left != null && right != null) {
if (left.val < right.val) {
curr.next = left;
left = left.next;
} else {
curr.next = right;
right = right.next;
}
curr = curr.next;
}
if (left != null) {
curr.next = left;
} else if (right != null) {
curr.next = right;
}
while (curr.next != null) {
curr = curr.next;
}
return curr;
}
|
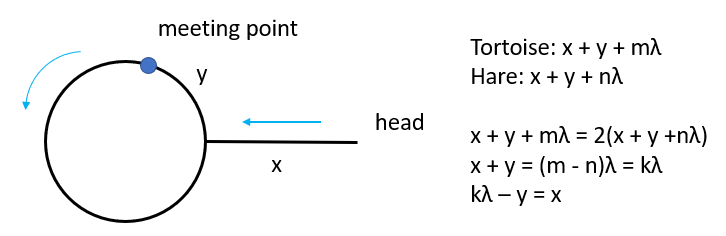
Cycle Detection
Floyd’s Tortoise and Hare
Linked List Cycle II
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode tortoise = head, hare = head;
while (hare != null && hare.next != null) {
tortoise = tortoise.next;
hare = hare.next.next;
// finds the first meeing point
if (tortoise == hare) {
// resets tortoise to head
tortoise = head;
while (tortoise != hare) {
tortoise = tortoise.next;
hare = hare.next;
}
return hare;
}
}
return null;
}
|
This algorithm can be used to detect duplicate elements in an array, too.
Find the Duplicate Number
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| int findDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
// Finds the first meeting point
int tortoise = nums[0], hare = nums[0];
do {
tortoise = nums[tortoise];
hare = nums[nums[hare]];
} while (tortoise != hare);
// Resets `tortoise` to head
tortoise = nums[0];
while (tortoise != hare) {
tortoise = nums[tortoise];
hare = nums[hare];
}
return hare;
}
|
A hidden condition is nums[0] != 0, otherwise the tortoise and hare will stay at 0 forever.
Happy Number
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| public boolean isHappy(int n) {
// finds meeting point
int tortoise = n, hare = getNext(n);
while (hare != 1 && tortoise != hare) {
tortoise = getNext(tortoise);
hare = getNext(getNext(hare));
}
return hare == 1;
}
private int getNext(int n) {
int sum = 0;
while (n > 0) {
sum += (n % 10) * (n % 10);
n /= 10;
}
return sum;
}
|
Reverse
Palindrome Linked List
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *fast = head, *slow = head;
while (fast && fast->next) {
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
// If there are n nodes in the list and the nodes are 0 indexed,
// then `slow` is at the (n / 2)-th node.
// Reverse the second half list: [n/2, n)
ListNode *prev = slow, *tmp = nullptr;
slow = slow->next;
prev->next = nullptr;
while (slow) {
tmp = slow->next;
slow->next = prev;
prev = slow;
slow = tmp;
}
// First node
fast = head;
// Last node
slow = prev;
while (slow) {
if (fast->val != slow->val) {
return false;
}
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return true;
}
|
Add Two Numbers II
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
| public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
return addTwoNumbers(l1, l2, size(l1), size(l2));
}
private ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2, int s1, int s2) {
if (s1 < s2) {
return addTwoNumbers(l2, l1, s2, s1);
}
// s1 >= s2
// adds the two lists with tails aligned
// carry is not considered yet
ListNode head = null, curr = null;
while (s1 > 0) {
// creates the result list in reverse order
curr = new ListNode(l1.val + (s1 > s2 ? 0 : l2.val));
curr.next = head;
head = curr;
if (s1-- == s2) {
s2--;
l2 = l2.next;
}
l1 = l1.next;
}
// normalization
head = null;
int carry = 0;
while (curr != null) {
curr.val += carry;
carry = curr.val / 10;
curr.val %= 10;
// reverses the result list on the fly
ListNode tmp = curr.next;
curr.next = head;
head = curr;
curr = tmp;
}
// adds a new head if carry exists
if (carry > 0) {
curr = new ListNode(1);
curr.next = head;
head = curr;
}
return head;
}
private int size(ListNode l) {
int s = 0;
while (l != null) {
l = l.next;
s++;
}
return s;
}
|
Clone
Copy List with Random Pointer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
Node curr = head, next = null;
// links each copy node to its original node
while (curr != null) {
next = curr.next;
Node copy = new Node(curr.val);
curr.next = copy;
copy.next = next;
curr = next;
}
// assigns random pointers for the copy nodes
curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
if (curr.random != null) {
curr.next.random = curr.random.next;
}
curr = curr.next.next;
}
curr = head;
Node dummyCopyHead = new Node(0);
Node copyCurr = dummyCopyHead, copyNext = null;
while (curr != null) {
// extracts the copy list
copyNext = curr.next;
copyCurr.next = copyNext;
copyCurr = copyNext;
// restores the original list
next = curr.next.next;
curr.next = next;
curr = next;
}
return dummyCopyHead.next;
}
|
Tree
Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return root;
}
Node leftmost = root;
while (leftmost.left != null) {
// starts from leftmost node in each level
Node head = leftmost;
while (head != null) {
// inner connection
head.left.next = head.right;
// inter connection
if (head.next != null) {
head.right.next = head.next.left;
}
head = head.next;
}
// moves to the next level
leftmost = leftmost.left;
}
return root;
}
|
Generalizing it with an arbitrary binary tree:
Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| // the previous node on the next level
// we're about to connect a new node as its next
private Node prev = null;
// leftmost node of the current level
private Node leftmost = null;
public Node connect(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return root;
}
leftmost = root;
Node curr = leftmost;
while (leftmost != null) {
curr = leftmost;
prev = leftmost = null;
while (curr != null) {
helper(curr.left);
helper(curr.right);
curr = curr.next;
}
}
return root;
}
private void helper(Node node) {
if (node != null) {
if (prev == null) {
// current node is the first node of the next level
leftmost = node;
} else {
// connects current node to the previous node
prev.next = node;
}
prev = node;
}
}
|
Double Linked List
Circular Double Linked List
Design Most Recently Used Queue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
| // sqrt decomposition
// seats are split to buckets
// nodes are items
// each bucket contains a circular double linked list of nodes
private Node[] buckets;
// count of nodes in each bucket
private int m;
public MRUQueue(int n) {
this.m = (int)Math.sqrt(n);
// Math.ceil(n / m)
this.buckets = new Node[(n + m - 1) / m];
for (int i = 0; i < buckets.length; i++) {
buckets[i] = new Node(0);
}
// bucket index for seat i: (i - 1) / m
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
buckets[(i - 1) / m].prepend(new Node(i));
}
}
public int fetch(int k) {
// bucket index for seat k: (k - 1) / m
Node node = buckets[(k - 1) / m].next;
// target seat index in the bucket: (k - 1) % m
for (int i = 0; i < (k - 1) % m; i++) {
node = node.next;
}
node.remove();
// for each bucket after the current bucket,
// moves one item to its previous bucket
for (int i = 1 + (k - 1) / m; i < buckets.length; i++) {
buckets[i - 1].prepend(buckets[i].next.remove());
}
buckets[buckets.length - 1].prepend(node);
return node.val;
}
class Node {
Node prev = this, next = this;
int val;
Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
// prepends `node` to this node
public void prepend(Node node) {
this.prev.next = node;
node.prev = this.prev;
this.prev = node;
node.next = this;
}
public Node remove() {
prev.next = next;
next.prev = prev;
return next = prev = this;
}
}
|