Line Sweep
Fundamentals
Line sweep is an algorithm to solve problems like The Skyline Problem. The key idea is to keep track of every change (delta) at each position, then linear scan and process the positions in the line. This delta is very similar to the pulses in Discrete Time Signal Processing.
There are two basic forms of algorithm. The first form is to use a list to record the deltas of all position, then sort the list with regard to positions. For each position, there can be more than one list element, and we consolidate them with another linear scan. For example:
Average Height of Buildings in Each Segment
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
public int[][] averageHeightOfBuildings(int[][] buildings) {
// {point, (+/-)height}
List<int[]> heights = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] b : buildings) {
heights.add(new int[]{b[0], b[2]});
heights.add(new int[]{b[1], -b[2]});
}
Collections.sort(heights, Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));
List<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
int sum = 0, count = 0;
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < heights.size(); i = j) {
// updates end of prev int[]
if (sum > 0) {
list.get(list.size() - 1)[1] = heights.get(i)[0];
}
// consolidates height sum and count at the current position
for (j = i; j < heights.size() && heights.get(i)[0] == heights.get(j)[0]; j++) {
sum += heights.get(j)[1];
count += heights.get(j)[1] > 0 ? 1 : -1;
}
// if any of the following is true, we need a new result block
// - empty list
// - curr != end of prev int[]
// - average != average of prev int[]
if (count > 0 &&
(list.isEmpty() ||
list.get(list.size() - 1)[1] != heights.get(i)[0] ||
list.get(list.size() - 1)[2] != sum / count)) {
list.add(new int[]{heights.get(i)[0], heights.get(i)[0], sum / count});
}
}
int[][] street = new int[list.size()][];
for (int i = 0; i < street.length; i++) {
street[i] = list.get(i);
}
return street;
}
Similarly, we can use a priority queue instead of list to avoid manual sorting. See example.
The second form is to use an array or an ordered map to store the deltas of all positions. The positions are used as keys, so the position of each entry is unique. The value of each entry is the consolidated deltas. For example:
Average Height of Buildings in Each Segment
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
public int[][] averageHeightOfBuildings(int[][] buildings) {
// {height sum, count}
Map<Integer, int[]> map = new TreeMap<>();
for (int[] b : buildings) {
if (map.containsKey(b[0])) {
map.get(b[0])[0] += b[2];
map.get(b[0])[1]++;
} else {
map.put(b[0], new int[]{b[2], 1});
}
if (map.containsKey(b[1])) {
map.get(b[1])[0] -= b[2];
map.get(b[1])[1]--;
} else {
map.put(b[1], new int[]{-b[2], -1});
}
}
List<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
int sum = 0, count = 0;
for (var e : map.entrySet()) {
int k = e.getKey();
int[] v = e.getValue();
// updates end of prev int[]
if (sum > 0) {
list.get(list.size() - 1)[1] = k;
}
// accumulates sum and count
sum += v[0];
count += v[1];
// if any of the following is true, we need a new result block
// - empty list
// - curr != end of prev int[]
// - average != average of prev int[]
if (count > 0 &&
(list.isEmpty() ||
list.get(list.size() - 1)[1] != k ||
list.get(list.size() - 1)[2] != sum / count)) {
list.add(new int[]{k, k, sum / count});
}
}
int[][] street = new int[list.size()][];
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
street[i] = list.get(i);
}
return street;
}
List/Priority Queue Form
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
public List<List<Integer>> getSkyline(int[][] buildings) {
List<int[]> heights = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] b: buildings) {
heights.add(new int[]{b[0], b[2]});
heights.add(new int[]{b[1], -b[2]});
}
// when positions are equal, sorts by height in descending order
// since exit has negative height, it ensures we meet the entry of a building before its exit
Collections.sort(heights, (a, b) -> a[0] == b[0] ? b[1] - a[1] : a[0] - b[0]);
// maintains all heights in the current position
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
int prev = 0;
// a trick to deal with the first building in a block
// (prev, min building height)
map.put(0, 1);
for (int[] h: heights) {
if (h[1] > 0) {
// enqueues on entry
map.put(h[1], map.getOrDefault(h[1], 0) + 1);
} else {
// dequeues on exit
map.put(-h[1], map.get(-h[1]) - 1);
map.remove(-h[1], 0);
}
// gets the max height
int curr = map.lastKey();
// no consecutive horizontal lines of equal height
if (prev != curr) {
list.add(Arrays.asList(h[0], curr));
prev = curr;
}
}
return list;
}
Array/Ordered Map Form
Array
Range Update with Prefix Sum
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public int[] getModifiedArray(int length, int[][] updates) {
int[] arr = new int[length];
// Finds pulses (diff array)
for (int[] u : updates) {
arr[u[0]] += u[2];
// +1 because the end is exclusive
if (u[1] + 1 < length) {
arr[u[1] + 1] -= u[2];
}
}
// Accumulates pulses
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
arr[i] += arr[i - 1];
}
return arr;
}
Count Positions on Street With Required Brightness
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public int meetRequirement(int n, int[][] lights, int[] requirement) {
int[] brightness = new int[n + 1];
for (int[] l : lights) {
brightness[Math.max(0, l[0] - l[1])]++;
brightness[Math.min(n, l[0] + l[1] + 1)]--;
}
int b = 0, count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
b += brightness[i];
if (b >= requirement[i]) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
Count the Number of Houses at a Certain Distance II
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
vector<long long> countOfPairs(int n, int x, int y) {
if (x > y) {
swap(x, y);
}
vector<long long> result(n);
// First, computes the diff array.
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// Each house can always connect to its neighbors with distance 1,
// even if n = 2.
// The +1 on each side keeps contributing to the number of pairs at distance > 0,
// until it meets an end.
result[0] += 2;
// Min distance (denoted as m) between the current house (house[i]) and house[1].
// Direct path: i - 1
// Path i -> y -> x -> 1: (abs(i - y)) + (1) + (x - 1)
//
// house[i] doesn't have pairs distances > m,
// so, it no longer affects the count beyond the distance m,
// As a result, decrement the diff array at m to reflect this change.
result[min(i - 1, abs(i - y) + x)]--;
// Min distance between house[i] and house[n].
// Direct path: n - i
// Path i -> x -> y -> n: (abs(i - x)) + (1) + (n - 1)
result[min(n - i, abs(i - x) + 1 + n - y)]--;
// Min distance between house[i] and x
// Direct path: abs(x - i)
// i -> y -> x: (abs(y - i)) + 1
// After reaching x, the path diverges so beyond this point there's an additional pair.
result[min(abs(i - x), abs(y - i) + 1)]++;
// See above
result[min(abs(i - x) + 1, abs(y - i))]++;
// Distance to the cycle.
// If x <= i <= y, house[i] already on the cycle.
int r = max(x - i, 0) + max(i - y, 0);
// Previously, the path diverges when reaching x or y.
// There are two cases on the cycle:
// 1. x -> y using the additional street and then reverse back to x using the normal streets
// and stop in the middle
// 2. x -> y using normal streets and stop in the middle
// There's a shorter path to nodes after the loop midpoint with the other path
// so, we should stop at the midpoint.
// The additional street between x and y leads to path divergence at x or y.
// There are two traversal scenarios on the cycle:
// 1. x -> y via the additional street, then returning towards x along the normal streets,
// and halting at the cycle's midpoint.
// (y - x + 1) / 2
// 2. x -> reaching y via normal streets, and stopping at the cycle's midpoint.
// (y - x) / 2
// The shortest path to houses past the cycle's midpoint may vary
// due to alternate routes via the additional street or normal streets.
// Therefore, distance calculations should consider paths only up to the cycle's midpoint,
// where the alternate route becomes shorter.
//
// e.g.
// if distance(x, y) = y - x = 4 (even), then 4 / 2 == (4 + 1) / 2 == 2;
// if distance(x, y) = y - x = 5 (odd), then 5 / 2 == 2, (5 + 1) / 2 == 3
result[r + (y - x + 0) / 2]--;
result[r + (y - x + 1) / 2]--;
}
// Second, builds the cumulative prefix sum array from the diff array.
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
result[i] += result[i - 1];
}
return result;
}
Ordered Map
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
public List<List<Long>> splitPainting(int[][] segments) {
Map<Integer, Long> map = new TreeMap<>();
for (int[] s : segments) {
map.put(s[0], map.getOrDefault(s[0], 0l) + s[2]);
map.put(s[1], map.getOrDefault(s[1], 0l) - s[2]);
}
List<List<Long>> painting = new ArrayList<>();
int prev = 0;
long color = 0;
for (int curr : map.keySet()) {
// color == 0 means this segment is not painted
if (prev > 0 && color > 0) {
painting.add(Arrays.asList((long)prev, (long)curr, color));
}
color += map.get(curr);
prev = curr;
}
return painting;
}
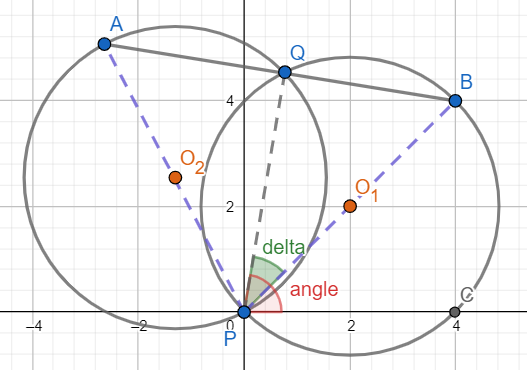
Arc Sweep
Maximum Number of Darts Inside of a Circular Dartboard
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
public int numPoints(int[][] points, int r) {
// at least 1 point can be included by the circle
int max = 1;
for (int[] p : points) {
// {angle, point count}
List<double[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int [] q : points) {
// for all q that are within 2r radius of p
if (p[0] != q[0] || p[1] != q[1]) {
double d = distance(p, q);
if (d <= 2 * r) {
// angle between line p-q and the positive x axis.
double angle = Math.atan2(q[1] - p[1], q[0] - p[0]);
// half of the span between entry and exit
double delta = Math.acos(d / (2 * r));
// entry
list.add(new double[]{angle - delta, 1});
// exit
list.add(new double[]{angle + delta, -1});
}
}
Collections.sort(list, (a, b) -> a[0] == b[0] ? Double.compare(b[1], a[1]) : Double.compare(a[0], b[0]));
// initial value == 1, which is p-q line
int count = 1;
for (var e : list) {
max = Math.max(max, count += e[1]);
}
}
}
return max;
}
private double distance(int[] p1, int[] p2) {
return Math.sqrt((p1[0] - p2[0]) * (p1[0] - p2[0]) + (p1[1] - p2[1]) * (p1[1] - p2[1]));
}
Maximum Number of Visible Points
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
public int visiblePoints(List<List<Integer>> points, int angle, List<Integer> location) {
// list of radian degrees
List<Double> list = new ArrayList<>();
int locationPoints = 0;
for (List<Integer> p : points) {
if (p.equals(location)) {
locationPoints++;
} else {
list.add(Math.toDegrees(Math.atan2(p.get(1) - location.get(1), p.get(0) - location.get(0))));
}
}
Collections.sort(list);
// circular
int n = list.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (list.get(i) < 0) {
list.add(list.get(i) + 360);
}
}
// sliding window
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0, j = 0; j < list.size(); j++) {
while (list.get(j) - list.get(i) > angle) {
i++;
}
max = Math.max(max, j - i + 1);
}
return max + locationPoints;
}