Geometry
Theorem
Triangle area using coordinates
\[T={\frac {1}{2}}{\big |}(x_{A}-x_{C})(y_{B}-y_{A})-(x_{A}-x_{B})(y_{C}-y_{A}){\big |}\]In a normed vector space \(V\), one of the defining properties of the norm is the triangle inequality:
\[\|x+y\|\leq \|x\|+\|y\|\quad \forall \,x,y\in V\]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public boolean escapeGhosts(int[][] ghosts, int[] target) {
// Manhattan distance
int d = Math.abs(target[0]) + Math.abs(target[1]);
for (int[] g : ghosts) {
if (Math.abs(g[0] - target[0]) + Math.abs(g[1] - target[1]) <= d) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
For three points \(P_{1}=(x_{1},y_{1})\), \(P_{2}=(x_{2},y_{2})\) and \(P_{3}=(x_{3},y_{3})\), compute the z-coordinate of the cross product of the two vectors \(\overrightarrow {P_{1}P_{2}}\) and \(\overrightarrow {P_{1}P_{3}}\), which is given by the expression \((x_{2}-x_{1})(y_{3}-y_{1})-(y_{2}-y_{1})(x_{3}-x_{1})\).
Overlapping
Circle and Rectangle Overlapping
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public boolean checkOverlap(int radius, int x_center, int y_center, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) {
// finds the closest point of the rectangle to the center.
// if the center is in the rectangle, the center itself is the point
int x = closest(x_center, x1, x2);
int y = closest(y_center, y1, y2);
int dx = x_center - x;
int dy = y_center - y;
return dx * dx + dy * dy <= radius * radius;
}
private int closest(int value, int min, int max) {
return Math.max(min, Math.min(max, value));
}
Area
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
public int minAreaRect(int[][] points) {
Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int[] p : points) {
map.computeIfAbsent(p[0], k -> new HashSet<>()).add(p[1]);
}
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < points.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
// diagnoal opposite points
int[] p1 = points[i], p2 = points[j];
// skips same x or y
if (p1[0] == p2[0] || p1[1] == p2[1]) {
continue;
}
int area = Math.abs(p1[0] - p2[0]) * Math.abs(p1[1] - p2[1]);
if (area > min) {
continue;
}
// computes diagonal points only
// confirms the other two points exist in the set
if (map.get(p1[0]).contains(p2[1]) && map.get(p2[0]).contains(p1[1])) {
min = area;
}
}
}
return min == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : min;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
public int minAreaRect(int[][] points) {
Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int[] p : points) {
map.computeIfAbsent(p[0], k -> new HashSet<>()).add(p[1]);
}
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < points.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
int[] p1 = points[i], p2 = points[j];
// skips same x or y
if (p1[0] == p2[0] || p1[1] == p2[1]) {
continue;
}
int area = Math.abs(p1[0] - p2[0]) * Math.abs(p1[1] - p2[1]);
if (area > min) {
continue;
}
// computes diagonal points only
// confirms the other two points exist in the set
if (map.get(p1[0]).contains(p2[1]) && map.get(p2[0]).contains(p1[1])) {
min = area;
}
}
}
return min == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : min;
}
Dihedral Group
Dihedral group: the group of symmetries of a regular polygon, which includes rotations and reflections.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
private static final int[][] DIRECTIONS = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
private static final int[][] TRANSFORMATIONS = {{1, 1}, {1, -1}, {-1, 1}, {-1, -1}};
private int[][] grid;
private int m, n;
private boolean[][] visited;
public int numDistinctIslands2(int[][] grid) {
this.grid = grid;
this.m = grid.length;
this.n = grid[0].length;
this.visited = new boolean[m][n];
Set<String> islands = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1 && !visited[i][j]) {
List<int[]> cells = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(i, j, cells);
islands.add(norm(cells));
}
}
}
return islands.size();
}
private void dfs(int i, int j, List<int[]> cells) {
if (i < 0 || i == m || j < 0 || j == n || grid[i][j] == 0 || visited[i][j]) {
return;
}
visited[i][j] = true;
cells.add(new int[]{i, j});
for (int[] d : DIRECTIONS) {
dfs(i + d[0], j + d[1], cells);
}
}
private String norm(List<int[]>cells) {
List<String> forms = new ArrayList<>();
// generates 8 different transformations:
// (x, y), (x, -y), (-x, y), (-x, -y)
// (y, x), (-y, x), (y, -x), (-y, -x)
for (int[] t : TRANSFORMATIONS) {
List<int[]> list1 = new ArrayList<>(), list2 = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] c : cells) {
list1.add(new int[]{c[0] * t[0], c[1] * t[1]});
list2.add(new int[]{c[1] * t[1], c[0] * t[0]});
}
forms.add(getKey(list1));
forms.add(getKey(list2));
}
// sorts the keys and uses the first one as the representative
Collections.sort(forms);
return forms.get(0);
}
private String getKey(List<int[]> cells) {
Collections.sort(cells, (a, b) -> a[0] == b[0] ? a[1] - b[1] : a[0] - b[0]);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int[] c : cells) {
// (x - x0, y - y0)
sb.append((c[0] - cells.get(0)[0]) + "#" + (c[1] - cells.get(0)[1]) + "#");
}
return sb.toString();
}
Distance
For a real number \(p \ge 1\), the \(p\)-norm or \(L^{p}\)-norm of \(x\) is defined by:
\[\lVert x \rVert_{p}=(|x_{1}|^{p}+|x_{2}|^{p}+\dots +|x_{n}|^{p})^{1/p}\]Taxicab Distance
Taxicab distance = Manhattan distance: \(L^1\)-norm
Maximum of Absolute Value Expression
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
public int maxAbsValExpr(int[] arr1, int[] arr2) {
int max = 0, n = arr1.length;
int[] coefficients = {-1, 1};
// |x[i] - x[j]| + |y[i] - y[j]| + |i - j| = f(j) - f(i)
// where f(i) = p * x[i] + q * y[i] + i
// with p = 1 or -1, q = 1 or -1
for (int p : coefficients) {
for (int q : coefficients) {
// origin point
int origin = p * arr1[0] + q * arr2[0] + 0;
// computes the Manhattan distance to the origin point
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int value = p * arr1[i] + q * arr2[i] + i;
max = Math.max(max, value - origin);
origin = Math.min(origin, value);
}
}
}
return max;
}
Maximum Manhattan Distance
\[\max_{i,j}Manhattan(P_i,P_j) = \max_{i,j}(\max(|s_i - s_j|,|d_i - d_j|))\]Euclidean Distance
Euclidean distance: \(L^2\)
Chebyshev Distance
Chebyshev distance = chessboard distance: \(L^{\infty}\)
Determine if a Cell Is Reachable at a Given Time
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
bool isReachableAtTime(int sx, int sy, int fx, int fy, int t) {
int dx = abs(sx - fx), dy = abs(sy - fy);
if (dx == 0 && dy == 0 && t == 1) {
return false;
}
// Chebyshev distance
// Move diagonally for min(dx, dy)
// Then go along the longer side
return min(dx, dy) + abs(dx - dy) <= t;
}
Geometric Median
Geometric median: \(L^1\) estimator.
\[{\underset {y\in \mathbb {R} ^{n}}{\operatorname {arg\,min} }}\sum _{i=1}^{m}\left\|x_{i}-y\right\|_{2}\]Weiszfeld’s algorithm
\[y_{i+1}=(\sum_{j=1}^{m}{\frac{x_{j}}{\|x_{j}-y_{i}\|}})/(\sum_{j=1}^{m}{\frac{1}{\|x_{j}-y_{i}\|}})\]Median
One-dimensional median is a special case of geometric median. It is the point about which the mean absolute deviation is minimized.
Mean absolute deviation of a set \(\\{x_1,x_2,\ldots,x_n\\}\):
\[\frac{1}{n}\sum _{i=1}^{n}|x_{i}-m(X)|\]Where \(m(X)\) is a measure of central tendency.
- Mean minimizes total distance for Euclidean distance:
- Mode minimizes distance for indicator function
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public int minTotalDistance(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
List<Integer> x = new ArrayList<>(), y = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
x.add(i);
}
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
y.add(j);
}
}
}
return minDistance1D(x) + minDistance1D(y);
}
private int minDistance1D(List<Integer> points) {
int d = 0, median = points.get(points.size() / 2);
for (int p : points) {
d += Math.abs(p - median);
}
return d;
}
Apply Operations to Maximize Frequency Score
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
nt maxFrequencyScore(vector<int>& nums, long long k) {
ranges::sort(nums);
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (j < nums.size()) {
// Median minimizes the sum of absolute deviation.
// nums[(i + j++) / 2] equals the median before j moves in.
// e.g. odd-size window
// i = 0, j = 3, window = [0,1,2]
// old median = 1
// new median = nums[(0 + 3) / 2] = 1
// e.g. even-size window
// i = 0, j = 2, window = [0,1]
// old median = 0 or 1
// new median = nums[(0 + 2) / 2] = 1
k -= nums[j] - nums[(i + j++) / 2];
if (k < 0) {
// Similarly, nums[(i + j) / 2] equals the median before i moves out.
k += nums[(i + j) / 2] - nums[i++];
}
}
return j - i;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
private static final int MAX = 100 * 10000;
public int minDistance(int[] houses, int k) {
int n = houses.length;
Arrays.sort(houses);
// finds the median of houses[i] to houses[j]
// calculates the distance
int[][] distance = new int[n + 1][n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
for (int m = i; m <= j; m++) {
distance[i][j] += Math.abs(houses[(i + j) / 2] - houses[m]);
}
}
}
// dp[m][i]: minimum total distance of m mailboxes starting from i-th house
int[][] dp = new int[k + 1][n + 1];
// initializes dp table boarders with max
Arrays.fill(dp[0], MAX);
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
dp[i][n] = MAX;
}
// initializes dp[0][n] with 0
dp[0][n] = 0;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int m = 1; m <= k; m++) {
dp[m][i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
// houses[i:] is split into two groups:
// houses[i:j] and houses[(j + 1):]
dp[m][i] = Math.min(dp[m][i], distance[i][j] + dp[m - 1][j + 1]);
}
}
}
return dp[k][0];
}
Another way to calculate the distance matrix:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
distance[i][j] = houses[j] - houses[i];
if (i + 1 < n - 1 && j > 0) {
// from houses[(i + 1):(j - 1)] to houses[i:j]
// the minimum distance added by the two new endpoints houses[i] and houses[j]
// equals houses[j] - houses[i]
// the mailbox can be at any point between the new endpoints
distance[i][j] += distance[i + 1][j - 1];
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
double findMedianSortedArrays(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
int m = nums1.size(), n = nums2.size();
if (m > n) {
return findMedianSortedArrays(nums2, nums1);
}
// left_part | right_part
// A[0], A[1], ..., A[i-1] | A[i], A[i+1], ..., A[m-1]
// B[0], B[1], ..., B[j-1] | B[j], B[j+1], ..., B[n-1]
// Binary searches the cut point in nums1
int low = 0, high = m;
while (low <= high) {
// len(left) == len(right)
// If m + n is even, i + j == m - i + n - j;
// otherwise, i + j == m - i + n - j + 1.
// Combines the above two cases:
// j == (m + n + 1) / 2 - i
unsigned int i = (low + high) >> 1, j = (m + n + 1) / 2 - i;
// Values on either side of the cut point of each array
int nums1Left = i == 0 ? numeric_limits<int>::min() : nums1[i - 1];
int nums1Right = i == m ? numeric_limits<int>::max() : nums1[i];
int nums2Left = j == 0 ? numeric_limits<int>::min() : nums2[j - 1];
int nums2Right = j == n ? numeric_limits<int>::max() : nums2[j];
// For each array, max(left) <= min(right)
if (nums1Left > nums2Right) {
high = i - 1;
} else if (nums2Left > nums1Right) {
low = i + 1;
} else {
int maxLeft = max(nums1Left, nums2Left);
int minRight = min(nums1Right, nums2Right);
return (m + n) % 2 ? maxLeft : ((maxLeft + minRight) / 2.0);
}
}
return -1;
}
Circle
Smallest Circle Problem
Smallest-circle problem: computing the smallest circle that contains all of a given set of points in the Euclidean plane.
Circum Circle Cartesian equation:
\[{\begin{aligned} S_{x}&={\frac {1}{2}}\det {\begin{bmatrix}|\mathbf {A} |^{2}&A_{y}&1\\|\mathbf {B} |^{2}&B_{y}&1\\|\mathbf {C} |^{2}&C_{y}&1\end{bmatrix}},\\[5pt] S_{y}&={\frac {1}{2}}\det {\begin{bmatrix}A_{x}&|\mathbf {A} |^{2}&1\\B_{x}&|\mathbf {B} |^{2}&1\\C_{x}&|\mathbf {C} |^{2}&1\end{bmatrix}},\\[5pt] a&=\det {\begin{bmatrix}A_{x}&A_{y}&1\\B_{x}&B_{y}&1\\C_{x}&C_{y}&1\end{bmatrix}},\\[5pt] b&=\det {\begin{bmatrix}A_{x}&A_{y}&|\mathbf {A} |^{2}\\B_{x}&B_{y}&|\mathbf {B} |^{2}\\C_{x}&C_{y}&|\mathbf {C} |^{2}\end{bmatrix}} \end{aligned}}\]Circumcenter: \(\frac{\mathbf{S}}{a}\)
Circumradius: \(\sqrt{\frac{b}{a} + \frac{\|\mathbf{S}\|^2}{a ^ 2}}\)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
public double[] outerTrees(int[][] trees) {
return welzl(trees, new ArrayList<>(), 0);
}
// Welzl's algorithm
private double[] welzl(int[][] p, List<int[]> r, int offset) {
if (offset == p.length || r.size() == 3) {
return trivial(r);
}
double[] circle = welzl(p, r, offset + 1);
if (isInside(circle, p[offset])) {
return circle;
}
// backtrack
r.add(p[offset]);
circle = welzl(p, r, offset + 1);
r.remove(r.size() - 1);
return circle;
}
private double[] trivial(List<int[]> r) {
if (r.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
if (r.size() == 1) {
return new double[] {r.get(0)[0], r.get(0)[1], 0};
}
if (r.size() == 2) {
return computeCircle2(r.get(0), r.get(1));
}
// if one angle is obtuse
// - (r[0], r[1])
// - (r[0], r[2])
// - (r[1], r[2])
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < 3; j++) {
double[] c = computeCircle2(r.get(i), r.get(j));
if (isInside(c, r.get(3 - i - j))) {
return c;
}
}
}
// circumscribed circle
return computeCircumscribedCircle(r.get(0), r.get(1), r.get(2));
}
// Compute the circle whose diameter is [p1, p2]
private double[] computeCircle2(int[] p1, int[] p2) {
double x1 = p1[0], y1 = p1[1], x2 = p2[0], y2 = p2[1];
double r2 = squaredDistance(p1, p2);
return new double[] {(x1 + x2) / 2, (y1 + y2) / 2, Math.sqrt(r2) / 2};
}
private double[] computeCircumscribedCircle(int[] p1, int[] p2, int[] p3) {
int a2 = squaredDistance(p1), b2 = squaredDistance(p2), c2 = squaredDistance(p3);
double sx = 0.5 * det(new double[][]{{a2, p1[1], 1}, {b2, p2[1], 1}, {c2, p3[1], 1}});
double sy = 0.5 * det(new double[][]{{p1[0], a2, 1}, {p2[0], b2, 1}, {p3[0], c2, 1}});
double a = det(new double[][]{{p1[0], p1[1], 1}, {p2[0], p2[1], 1}, {p3[0], p3[1], 1}});
double[] center = new double[]{sx / a, sy / a};
double r2 = squaredDistance(center, p1);
return new double[] {center[0], center[1], Math.sqrt(r2)};
}
private boolean isInside(double[] circle, int[] point) {
if (circle == null) {
return false;
}
return squaredDistance(circle, point) <= circle[2] * circle[2];
}
// Squared Euclidean distance
private int squaredDistance(int[] p1, int[] p2) {
return (p1[0] - p2[0]) * (p1[0] - p2[0]) + (p1[1] - p2[1]) * (p1[1] - p2[1]);
}
private int squaredDistance(int[] p) {
return p[0] * p[0] + p[1] * p[1];
}
private double squaredDistance(double[] p1, int[] p2) {
return (p1[0] - p2[0]) * (p1[0] - p2[0]) + (p1[1] - p2[1]) * (p1[1] - p2[1]);
}
// Determinant of 3 x 3 matrix
private double det(double[][] a) {
double x = (a[1][1] * a[2][2]) - (a[2][1] * a[1][2]);
double y = (a[1][0] * a[2][2]) - (a[2][0] * a[1][2]);
double z = (a[1][0] * a[2][1]) - (a[2][0] * a[1][1]);
return a[0][0] * x - a[0][1] * y + a[0][2] * z;
}
Rectangle
Find the indexes of four edges.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
// {up, left, down, right}
Map<Integer, int[]> edges = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
edges.putIfAbsent(targetGrid[i][j], new int[]{m, n, -1, -1});
int[] p = edges.get(targetGrid[i][j]);
p[0] = Math.min(p[0], i);
p[1] = Math.min(p[1], j);
p[2] = Math.max(p[2], i);
p[3] = Math.max(p[3], j);
}
}
Convex Hull
Monotone Chain: Andrew’s monotone chain convex hull algorithm constructs the convex hull of a set of 2-dimensional points in \(O(n\log n)\) time. It does so by first sorting the points lexicographically (first by x-coordinate, and in case of a tie, by y-coordinate), and then constructing upper and lower hulls of the points in \(O(n)\) time.
Orientation of a Simple Polygon
\[\mathbf {O} ={\begin{bmatrix}1&x_{A}&y_{A}\\1&x_{B}&y_{B}\\1&x_{C}&y_{C}\end{bmatrix}}\] \[\det(O)=(x_{B}-x_{A})(y_{C}-y_{A})-(x_{C}-x_{A})(y_{B}-y_{A})\]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
// Convex Hull
// Monotone Chain
public int[][] outerTrees(int[][] points) {
// sort the point of P by x-coordinate
// in case of a tie, by y-coordinate
Arrays.sort(points, (a, b) -> a[0] == b[0] ? a[1] - b[1] : a[0] - b[0]);
// holds the vertices of upper and lower hulls
List<int[]> lower = new ArrayList<>(), upper = new ArrayList<>();
// builds Lower layer of hulls
for (int[] p : points) {
// while the 3 points are clockwise turn
while (lower.size() >= 2 &&
clockwise(lower.get(lower.size() - 2), lower.get(lower.size() - 1), p)) {
lower.remove(lower.size() - 1); // remove q on (p,q,r)
}
lower.add(p);
}
// builds upper layer of hulls
for (int i = points.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// while the 3 points are clockwise turn
while (upper.size() >= 2 &&
clockwise(upper.get(upper.size() - 2), upper.get(upper.size() - 1), points[i])) {
upper.remove(upper.size() - 1); // remove q on (p,q,r)
}
upper.add(points[i]);
}
// concatenates L and U to obtain the convex hull of P.
// points in the result will be listed in counter-clockwise order.
// removes duplicates.
Set<int[]> set = Stream.concat(lower.stream(), upper.stream())
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
int[][] perimeter = new int[set.size()][2];
int i = 0;
for (int[] p : set) {
perimeter[i++] = p;
}
return perimeter;
}
// orientation
private boolean clockwise(int[] a, int[] b, int[] c) {
return (b[1] - a[1]) * (c[0] - b[0]) - (b[0] - a[0]) * (c[1] - b[1]) > 0;
}
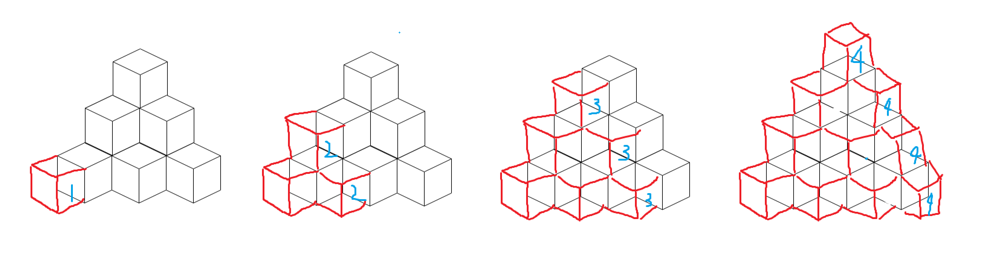
3-D
To build the extra boxes:
@SuperWhw:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public int minimumBoxes(int n) {
// sum = 1 + (1 + 2) + (1 + 2 + 3) + ... + (1 + 2 + ... + j)
int sum = 0, i = 0, j = 0;
while (sum < n) {
sum += i += ++j;
}
if (sum == n) {
return i;
}
// build extra boxes
sum -= i;
i -= j;
j = 0;
while (sum < n) {
sum += ++j;
}
return i + j;
}