Fenwick Tree
Fenwick Tree
Fenwick tree (Binary indexed tree)
A Fenwick tree or binary indexed tree is a data structure that can efficiently update elements and calculate prefix sums in a table of numbers.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
public class FenwickTree {
private int[] nums;
private int size;
public FenwickTree(int size) {
this.size = size;
// one-based indexing is assumed
nums = new int[size + 1];
}
/**
* Returns the sum of the input elements with index from 1 to i (one-based indexing)
* O(log(n))
* @param i upper index of the range (one-based indexing)
* @return sum of the input elements with index from 1 to i (one-based indexing)
*/
public int sum(int i) {
int sum = 0;
while (i > 0) {
sum += nums[i];
i -= lsb(i);
}
return sum;
}
/**
* Adds k to the input element with index i (one-based indexing)
* O(log(n))
* @param i index of the input element (one-based indexing)
* @param k number to be added to the element
*/
public void add(int i, int k) {
while (i <= size) {
nums[i] += k;
i += lsb(i);
}
}
private int lsb(int i) {
return i & (-i);
}
}
Count of Smaller Numbers After Self
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public List<Integer> countSmaller(int[] nums) {
// deduplication
// if i != j && nums[i] == nums[j]
// i and j should occupy only one position in the Fenwick Tree
Set<Integer> set = new TreeSet<>();
for (int num : nums) {
set.add(num);
}
int i = 0;
Map<Integer, Integer> indices = new HashMap<>();
for (int num : set) {
indices.put(num, i++);
}
FenwickTree ft = new FenwickTree(indices.size());
int n = nums.length;
List<Integer> counts = new ArrayList<>(n);
for (int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
int index = indices.get(nums[j]);
// `index` + 1 is the one-based index of nums[j]
// so the index of max smaller number is `index`
counts.add(0, ft.sum(index));
ft.add(index + 1, 1);
}
return counts;
}
This problem can be solved by Merge Sort, too.
Similar problem:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
public int reversePairs(int[] nums) {
// deduplication
// if i != j && nums[i] == nums[j]
// i and j should occupy only one position in the Fenwick Tree
Set<Integer> set = new TreeSet<>();
for (int num : nums) {
set.add(num);
}
int i = 0;
Map<Integer, Integer> indices = new HashMap<>();
for (int num : set) {
indices.put(num, i++);
}
FenwickTree ft = new FenwickTree(indices.size());
int count = 0;
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(set);
for (int j = nums.length - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
// index of the pair of nums[j]
int p = binarySearch(list, nums[j]);
if (p >= 0) {
count += ft.sum(indices.get(list.get(p)) + 1);
}
ft.add(indices.get(nums[j]) + 1, 1);
}
return count;
}
private int binarySearch(List<Integer> list, int target) {
int low = 0, high = list.size() - 1;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high + 1) >>> 1;
if (2l * list.get(mid) < target) {
low = mid;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return 2l * list.get(low) < target ? low : -1;
}
This problem can be solved by Merge Sort, too.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
private int MAX_RATING = (int)1e5;
public int numTeams(int[] rating) {
FenwickTree left = new FenwickTree(MAX_RATING), right = new FenwickTree(MAX_RATING);
// bucket counting
// in the beginning, the middle soldier is at -1
for (int r : rating) {
right.add(r, 1);
}
int count = 0;
for (int r : rating) {
right.add(r, -1);
count += left.sum(r - 1) * (right.sum(MAX_RATING) - right.sum(r)); // ascending
count += (left.sum(MAX_RATING) - left.sum(r)) * right.sum(r - 1); // descending
left.add(r, 1);
}
return count;
}
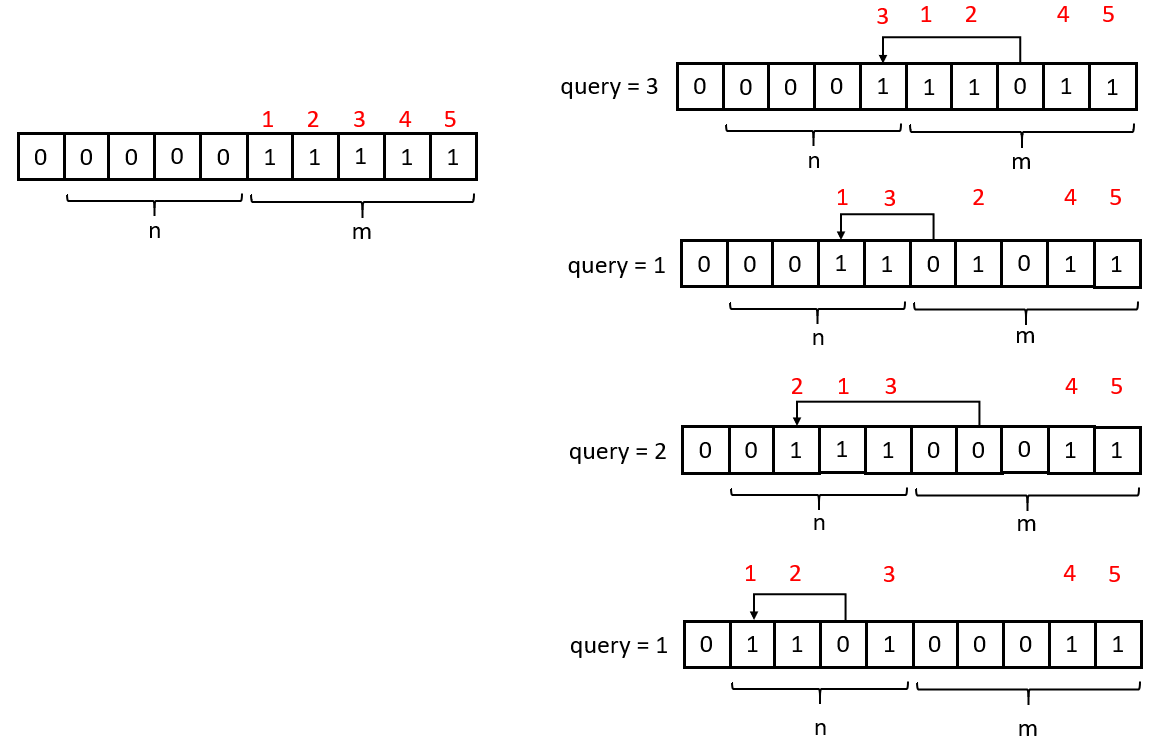
Queries on a Permutation With Key
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
public int[] processQueries(int[] queries, int m) {
int n = queries.length;
FenwickTree ft = new FenwickTree(n + m);
int[] index = new int[m];
// fills the last m positions with 1
// [1...n] is default to 0
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
ft.add(n + i, 1);
// memorizes index of the current element
index[i - 1] = n + i;
}
int[] result = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {
int curr = index[queries[i] - 1];
result[i] = ft.sum(curr) - 1;
// relocates queries[i] to a position in [1...n] in reverse order
int next = n - i;
ft.add(curr, -1);
ft.add(next, 1);
// updates the index of queries[i]
index[queries[i] - 1] = next;
}
return result;
}
Create Sorted Array through Instructions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
private static final int MOD = (int)1e9 + 7;
public int createSortedArray(int[] instructions) {
FenwickTree ft = new FenwickTree(Arrays.stream(instructions).max().getAsInt());
int cost = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < instructions.length; i++) {
cost = (int)(cost + Math.min(ft.sum(instructions[i] - 1), i - ft.sum(instructions[i])) % MOD) % MOD;
ft.add(instructions[i], 1);
}
return cost;
}
Minimum Possible Integer After at Most K Adjacent Swaps On Digits
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
public String minInteger(String num, int k) {
// index of each digit
List<Queue<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>(10);
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++) {
list.add(new LinkedList<>());
}
int n = num.length();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
list.get(num.charAt(i) - '0').offer(i);
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
FenwickTree ft = new FenwickTree(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// at current location, attempts to place 0...9
for (int d = 0; d <= 9; d++) {
if (list.get(d).size() != 0) {
// finds the first occurrence of d
int index = list.get(d).peek();
// since a few numbers already shifted to left, this index might be outdated.
// finds how many numbers got shifted to the left of index
// e.g. "4192", k = 3
// Round #1: d = 1, index = 1, shift = 0, "1492"
// Round #2: d = 2, index = 3, shift = 1, "1249"
int shift = ft.sum(index);
// (index - shift) is number of swaps to make d move from index to i
// ensures the d is in the k-size sliding window
if (index - shift <= k) {
k -= index - shift;
// the "shift" value (calculated by ft.sum(num)) of all nums to the right of index
// would increase by 1
ft.add(index + 1, 1);
list.get(d).poll();
sb.append(d);
break;
}
}
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
2D
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
private FenwickTree ft;
private int[][] nums;
public NumMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
if (matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return;
}
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
this.nums = new int[m][n];
this.ft = new FenwickTree(m, n);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
update(i, j, matrix[i][j]);
}
}
}
public void update(int row, int col, int val) {
ft.add(row + 1, col + 1, val - nums[row][col]);
nums[row][col] = val;
}
public int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) {
return ft.sum(row2 + 1, col2 + 1) - ft.sum(row1, col2 + 1) - ft.sum(row2 + 1, col1) + ft.sum(row1, col1);
}
public class FenwickTree {
private int[][] grid;
private int m, n;
public FenwickTree(int m, int n) {
this.m = m;
this.n = n;
// one-based indexing is assumed
grid = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
}
// Returns the sum from index (1, 1) to (row, col)
public int sum(int row, int col) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = row; i > 0; i -= lsb(i)) {
for (int j = col; j > 0; j -= lsb(j)) {
sum += grid[i][j];
}
}
return sum;
}
// Adds k to element with index (row, col)
public void add(int row, int col, int k) {
for (int i = row; i <= m; i += lsb(i)) {
for (int j = col; j <= n; j += lsb(j)) {
grid[i][j] += k;
}
}
}
private int lsb(int i) {
return i & (-i);
}
}
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.