Binary Search
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
int low = 0, high = nums.length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
return mid;
}
if (nums[mid] < target) {
low = mid + 1;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
Template
@zhijun_liao
Minimize x, s.t. condition(x) == true
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public int binarySearch(int[] arr) {
int low = min(searchSpace), high = max(searchSpace);
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
if (condition(mid)) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return low;
}
// f(x) is monotonically increasing
private boolean condition(int x) {
return f(x) >= 0;
}
Similarly,
Maximize x, s.t. condition(x) == true
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public int binarySearch(int[] arr) {
int low = min(searchSpace), high = max(searchSpace);
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high + 1) >>> 1;
if (condition(mid)) {
low = mid;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return low;
}
// f(x) is monotonically decreasing
private boolean condition(int x) {
return f(x) >= 0;
}
There can be variants of this template. For example: First Bad Version, The K Weakest Rows in a Matrix
low <= high,low < high, …low = mid + 1,low = mid, …high = mid - 1,high = mid, …return -1,return low,return high, …
Function
The function must be monotonic (or at least locally monotonic).
While Condition
while (low < high) is a better choice. The while loop only exits when low == high, which means there’s only one element left.
Boundary
The initial boundary [low, high] should include all possible answers. When each loop begins, any value within the range [low, high] could be the answer.
Mid
1
2
mid = low + (high - low) / 2; // lower mid
mid = low + (high - low + 1) / 2; // upper mid
To avoid infinite loop, here’s a rule of thumb:
- lower mid:
low = mid + 1andhigh = mid - upper mid:
low = midandhigh = mid - 1
Boundary Update
Rule of thumb: always use a logic that you can exclude mid.
1
2
3
4
5
if (nums[mid] > target) {
high = mid - 1;
} else {
low = mid;
}
1
2
3
4
5
if (nums[mid] < target) {
low = mid + 1;
} else {
high = mid;
}
To understand the corner cases, test your code with these examples: [0], [0, 1], [0, 1, 2] and [0, 1, 2, 3].
Variants
Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public int findMin(int[] nums) {
int low = 0, high = nums.length - 1;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
if (nums[mid] < nums[high]) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return nums[low];
}
Single Element in a Sorted Array
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public int singleNonDuplicate(int[] nums) {
int low = 0, high = nums.length - 1;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
// binary search on even indexes only
if (mid % 2 == 1) {
mid--;
}
if (nums[mid] == nums[mid + 1]) {
low = mid + 2;
} else {
high = mid;
}
}
return nums[low];
}
Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array II
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
public int findMin(int[] nums) {
int low = 0, high = nums.length - 1;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (nums[mid] > nums[high]) {
low = mid + 1;
} else if (nums[mid] < nums[high]) {
high = mid;
} else {
// finds the pivot index
if (nums[high - 1] > nums[high]) {
low = high;
break;
}
high--;
}
}
return nums[low];
}
Search in Rotated Sorted Array
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
int minIndex = findMinIndex(nums);
if (target == nums[minIndex]) {
return minIndex;
}
int n = nums.length, low = minIndex, high = minIndex - 1 + n;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
if (nums[mid % n] >= target) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return nums[low % n] == target ? low % n : -1;
}
private int findMinIndex(int[] nums) {
int low = 0, high = nums.length - 1;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
if (nums[mid] < nums[high]) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return low;
}
Search in Rotated Sorted Array II
Local Monotocity
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public int findPeakElement(int[] nums) {
int low = 0, high = nums.length - 1;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
if (nums[mid] > nums[mid + 1]) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return low;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public int[] findPeakGrid(int[][] mat) {
// binary search on columns
int low = 0, high = mat[0].length - 1;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
int row = findMaxRow(mat, mid);
if (mat[row][mid] > mat[row][mid + 1]) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return new int[]{findMaxRow(mat, low), low};
}
// finds the max row in column mid
private int findMaxRow(int[][] mat, int col) {
int row = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < mat.length; i++) {
if (mat[i][col] > mat[row][col]) {
row = i;
}
}
return row;
}
Generalization
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
int low = 0, high = nums.length;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
if (nums[mid] >= target) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return low;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public int minEatingSpeed(int[] piles, int h) {
int low = 1, high = Arrays.stream(piles).max().getAsInt(), target = h - piles.length;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < piles.length; i++) {
// Math.ceil((double)x / n) == (x - 1) / n + 1
sum += (piles[i] - 1) / mid;
if (sum > target) {
break;
}
}
if (sum > target) {
low = mid + 1;
} else {
high = mid;
}
}
return low;
}
Kth Smallest Element in a Sorted Matrix
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
// O(n * log(max - min))
public int kthSmallest(int[][] matrix, int k) {
int low = matrix[0][0], high = matrix[matrix.length - 1][matrix[0].length - 1];
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
if (condition(matrix, mid, k)) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return low;
}
private boolean condition(int[][] matrix, int value, int k) {
// starts from top-right
int count = 0, i = 0, j = matrix[0].length - 1;
while (i < matrix.length && j >= 0) {
if (matrix[i][j] > value) {
j--;
} else {
count += j + 1;
i++;
}
}
return count >= k;
}
Variant:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
public int[] kthSmallestPrimeFraction(int[] A, int K) {
double low = 0, high = 1;
int p = 0, q = 1;
int count = 0;
while (count != K) {
double mid = (low + high) / 2;
// starts from top-right
int i = 0, j = A.length - 1;
count = 0; // count of fractions less than mid
p = 0;
while (i < A.length && j >= 0) {
if (A[i] > mid * A[A.length - 1 - j]) {
j--;
} else {
// p / q < curr
// finds the largest fraction less than mid
if (p * A[A.length - 1 - j] < q * A[i]) {
p = A[i];
q = A[A.length - 1 - j];
}
count += j + 1;
i++;
}
}
if (count < K) {
low = mid;
} else if (count > K) {
high = mid;
}
}
return new int[]{p, q};
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public int findKthPositive(int[] arr, int k) {
int low = 0, high = arr.length;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
// if there's no missing positive integer in index range [0, i]
// arr[i] == i + 1
//
// let a[i] = arr[i] - i - 1
// a[i] is the number of missing positive integers
// a[i + 1] - a[i] == arr[i + 1] - (i + 1) - 1 - (arr[i] - i - 1)
// == arr[i + 1] - arr[i] - 1 >= 0
// so a[i] is increasing
if (arr[mid] - mid - 1 >= k) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
// kth -> +k
return low + k;
}
Missing Element in Sorted Array
Missing Number In Arithmetic Progression
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
public int missingNumber(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length, d = (arr[n - 1] - arr[0]) / n, low = 0, high = n;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
if (arr[mid] == arr[0] + d * mid) {
// it's easy to prove arr[i] - arr[0] - d * i is monotonic
// no matter whether d >= 0 or d < 0
// all numbers up to mid are present
low = mid + 1;
} else {
// a number is missing <= mid
high = mid;
}
}
return arr[0] + d * low;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
public int hIndex(int[] citations) {
int low = 0, high = citations.length;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
if (condition(citations, mid)) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return citations.length - low;
}
/**
* Checks if the author has (N - lower) papers that have at least (N - lower) citations each.
* @param lower number of papers with lower citations. When h is valid, lower == N - h
* @return true if the condition is met, otherwise false
*/
private boolean condition(int[] citations, int lower) {
// a[i] = citations[i] + i
// a[i + 1] - a[i] == citations[i + 1] + (i + 1) - (citations[i] + i)
// == citations[i + 1] - citations[i] + 1 > 0
// so a[i] is strictly increasing
//
// 1. citations[N - h] >= h: h of his/her N papers have at least h citations each
// 2. citations[N - h - 1] <= h: the other N - h papers have no more than h citations each
//
// Now we will prove we only need to finds the minimum value of lower that satisfies #1.
// If #1 is true, we have:
// h == citations.length - lower
// citations[lower] == h
//
// Then #2 is true, too:
// citations[N - h - 1] = citations[lower - 1] <= citations[lower] == h
return citations[lower] >= citations.length - lower;
}
Minimum Number of Days to Make m Bouquets
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
public int minDays(int[] bloomDay, int m, int k) {
int max = 0;
for (int d : bloomDay) {
max = Math.max(max, d);
}
if (bloomDay.length < m * k) {
return -1;
}
int low = 1, high = max;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
if (condition(bloomDay, m, k, mid)) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return low;
}
private boolean condition(int[] bloomDay, int m, int k, int day) {
int bouquet = 0, flower = 0;
for (int d : bloomDay) {
if (d <= day) {
if (++flower % k == 0) {
bouquet++;
}
} else {
flower = 0;
}
}
return bouquet >= m;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
public int splitArray(int[] nums, int m) {
int sum = 0, max = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
sum += num;
max = Math.max(max, num);
}
int low = max, high = sum;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
if (condition(nums, mid, m)) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return low;
}
/**
* Check whether with the given largest subarray sum, the array can be split into m subrrays.
* @param nums original array
* @param s largest subarray sum
* @param m number of subarrays
* @return true if the array can be split into m subarrays, otherwise false
*/
private boolean condition(int[] nums, int s, int m) {
int count = 1, sum = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
if (sum + num > s) {
count++;
sum = 0;
}
sum += num;
}
// count is the min number of subarrays that nums can be split into
// and the sum of each subarray is no more than s
return count <= m;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
public List<List<String>> suggestedProducts(String[] products, String searchWord) {
Arrays.sort(products);
List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= searchWord.length(); i++) {
int low = 0, high = products.length - 1;
String prefix = searchWord.substring(0, i);
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
if (condition(products, mid, prefix)) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = low; j < Math.min(low + 3, products.length); j++) {
if (products[j].startsWith(prefix)) {
list.add(products[j]);
}
}
result.add(list);
}
return result;
}
private boolean condition(String[] products, int index, String prefix) {
return products[index].compareTo(prefix) >= 0;
}
Search for the first index from which the k-element sliding window starts.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public List<Integer> findClosestElements(int[] arr, int k, int x) {
int low = 0, high = arr.length - k;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
if (arr[mid + k] - x >= x - arr[mid]) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return Arrays.stream(arr, low, low + k).boxed().collect(Collectors.toList());
}
Minimum Limit of Balls in a Bag
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public int minimumSize(int[] nums, int maxOperations) {
int low = 1, high = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
if (condition(nums, mid, maxOperations)) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return low;
}
private boolean condition(int[] nums, int penalty, int maxOperations) {
int operations = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
operations += (num - 1) / penalty;
}
// (maxOperations - operations) is monotonically increasing with respect to penalty
return operations <= maxOperations;
}
Maximum Value at a Given Index in a Bounded Array
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public int maxValue(int n, int index, int maxSum) {
int low = 0, high = maxSum;
while (low < high) {
int mid = low + (high - low + 1) / 2;
if (condition(mid, n, index, maxSum)) {
low = mid;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return low;
}
private boolean condition(int x, int n, int index, long maxSum) {
return sum(x, n, index) <= maxSum;
}
private long sum(int x, int n, int index) {
return f(x, index + 1) + f(x, n - index) - x;
}
// formula: (1 + n) * n / 2
private long f(int x, int n) {
// x > n: 2,3,
// x < n: 1,1,1,2,3
return x > n ? (long)(x + (x - n + 1)) * n / 2 : (long)(1 + x) * x / 2 + (n - x);
}
Maximum Number of Removable Characters
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
public int maximumRemovals(String s, String p, int[] removable) {
int low = 0, high = removable.length;
while (low < high) {
int mid = low + (high - low + 1) / 2;
if (condition(s, p, removable, mid)) {
low = mid;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return low;
}
private boolean condition(String s, String p, int[] removable, int k) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
set.add(removable[i]);
}
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < s.length() && j < p.length()) {
if (!set.contains(i) && s.charAt(i) == p.charAt(j)) {
j++;
}
i++;
}
return j == p.length();
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
public int maximizeSweetness(int[] sweetness, int k) {
int low = 1, high = (int)1e9 / (k + 1);
while (low < high) {
int mid = low + (high - low + 1) / 2;
if (condition(sweetness, mid, k)) {
low = mid;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return low;
}
private boolean condition(int[] sweetness, int minTotal, int k) {
int sum = 0, pieces = 0;
for (int s : sweetness) {
if ((sum += s) >= minTotal) {
sum = 0;
pieces++;
}
}
return pieces - k - 1 >= 0;
}
Maximum Font to Fit a Sentence in a Screen
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
public int maxFont(String text, int w, int h, int[] fonts, FontInfo fontInfo) {
int low = 0, high = fonts.length - 1;
while (low < high) {
int mid = low + (high - low + 1) / 2;
if (condition(text, w, h, fonts, mid, fontInfo)) {
low = mid;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return condition(text, w, h, fonts, low, fontInfo) ? fonts[low] : -1;
}
private boolean condition(String text, int w, int h, int[] fonts, int index, FontInfo fontInfo) {
int font = fonts[index];
if (fontInfo.getHeight(font) > h) {
return false;
}
int sum = 0;
for (char c : text.toCharArray()) {
sum += fontInfo.getWidth(font, c);
}
return sum <= w;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public int maxWidthRamp(int[] A) {
// decreasing list
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < A.length; i++) {
int n = list.size();
if (n == 0 || A[i] < A[list.get(n - 1)]) {
list.add(i);
} else {
// binary searches for the first element
// which is no greater than A[i]
int low = 0, high = n - 1;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
if (A[list.get(mid)] <= A[i]) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
max = Math.max(max, i - list.get(low));
}
}
return max;
}
Last Day Where You Can Still Cross
Binary Search + BFS/DFS
Fraction
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
private static final double MAX_ERROR = 1e-5;
public double findMaxAverage(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
double min = nums[0], max = nums[0];
for (int num : nums) {
if (num < min) {
min = num;
}
if (num > max) {
max = num;
}
}
// binary search the max avg between min and max
while (min + MAX_ERROR < max) {
double mid = (min + max) / 2;
if (hasAvgAbove(nums, k, mid)) {
min = mid;
} else {
max = mid;
}
}
return min;
}
// Checks if there exists a subarray of nums whose length >= k
// and its average >= target
private boolean hasAvgAbove(int[] nums, int k, double target) {
// avg(nums[i...j])
// => (nums[i] + nums[i + 1] + ... + nums[j]) / (j - i + 1) >= target
// => nums[i] + nums[i + 1] + ... + nums[j] >= target * (j - i + 1)
// => (nums[i] - target) + (nums[i + 1] - target) + ... + (nums[j] - target) >= 0
//
// sum is monotonically decreasing (in terms of target)
double sum = 0, outOfWindowSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
sum += nums[i] - target;
}
// sliding window
int i = k;
while (i < nums.length) {
if (sum >= 0) {
return true;
}
sum += nums[i] - target;
outOfWindowSum += nums[i - k] - target;
// if out-of-windows sum is negative, subtract it
if (outOfWindowSum < 0) {
sum -= outOfWindowSum;
outOfWindowSum = 0;
}
i++;
}
return sum >= 0;
}
Minimize Max Distance to Gas Station
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
private static final double MAX_ERROR = 1e-6;
public double minmaxGasDist(int[] stations, int k) {
int n = stations.length;
double low = 0, high = stations[n - 1] - stations[0];
while (low + MAX_ERROR < high) {
double mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (condition(stations, k, mid)) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid;
}
}
return low;
}
private boolean condition(int[] stations, int k, double penalty) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < stations.length - 1; i++) {
// keeps mid as max
count += Math.ceil((stations[i + 1] - stations[i]) / penalty) - 1;
}
// (k - count) is monitonically increasing wrt penalty
return count <= k;
}
Geometry
Minimum Time For K Virus Variants to Spread
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
private static final int MAX_POINT = 100;
public int minDayskVariants(int[][] points, int k) {
int low = 0, high = MAX_POINT * MAX_POINT;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
if (condition(points, mid, k)) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return low;
}
private boolean condition(int[][] points, int days, int k) {
for (int x = 1; x <= MAX_POINT; x++) {
for (int y = 1; y <= MAX_POINT; y++) {
int count = 0;
for (int[] p : points) {
// Manhattan distance
if (days >= Math.abs(x - p[0]) + Math.abs(y - p[1])) {
count++;
}
}
if (count >= k) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
Pour Water Between Buckets to Make Water Levels Equal
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
private boolean condition(int[] buckets, int loss, double w) {
double in = 0, out = 0;
for (int b : buckets) {
if (b < w) {
in += w - b;
} else {
out += b - w;
}
}
return out * (1 - loss / 100d) >= in;
}
Greedy
Maximum Number of Tasks You Can Assign
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
public int maxTaskAssign(int[] tasks, int[] workers, int pills, int strength) {
Arrays.sort(tasks);
Arrays.sort(workers);
// finds the smallest k tasks that can be assigned
int low = 0, high = Math.min(tasks.length, workers.length);
while (low < high) {
int mid = low + (high - low + 1) / 2;
if (condition(tasks, workers, pills, strength, mid)) {
low = mid;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return low;
}
private boolean condition(int[] tasks, int[] workers, int pills, int strength, int k) {
int m = workers.length;
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
map.put(workers[m - 1 - i], map.getOrDefault(workers[m - 1 - i], 0) + 1);
}
int count = 0;
// assigns tasks [0, k) in descending order
for (int i = k - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// attempts to assign the task to the strongest worker without the pill
var e1 = map.lastEntry();
int k1 = e1.getKey();
if (tasks[i] <= k1) {
map.put(k1, e1.getValue() - 1);
map.remove(k1, 0);
continue;
}
// attempts to assign the task to a worker with the pill
// number of workers with pills exceeds limit
if (count++ == pills) {
return false;
}
// worker >= task - strength
var e2 = map.ceilingEntry(tasks[i] - strength);
// impossible to assign the task, or
if (e2 == null) {
return false;
}
int k2 = e2.getKey();
map.put(k2, e2.getValue() - 1);
map.remove(k2, 0);
}
return true;
}
Combination
Ways to Split Array Into Three Subarrays
Nested Binary Search
Median of a Row Wise Sorted Matrix
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
public int matrixMedian(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
int low = 1, high = (int)1e6, k = m * n / 2 + 1;
while (low < high) {
// attempts mid as median
int mid = (low + high + 1) >>> 1, count = 0;
for (int[] row : grid) {
// since the helper function returns the min index so that row[index] >= mid,
// ALL row elements that >= mid will be counted
// this is why we count the right half rather than the left half
// (if the helper function returns the max index so that row[index] <= mid,
// we count the left helf instead)
count += n - binarySearch(row, mid);
}
if (count >= k) {
low = mid;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return low;
}
// binary searches for the min index so that nums[index] >= target.
// if all nums elements < target, returns n
private int binarySearch(int[] nums, int target) {
int n = nums.length, low = 0, high = n - 1;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
if (nums[mid] >= target) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return nums[low] >= target ? low : n;
}
Java
Arrays
If the range contains multiple elements equal to the specified object, there is no guarantee which one will be found.
Returns:
index of the search key, if it is contained in the array within the specified range; otherwise, (-(insertion point) - 1). The insertion point is defined as the point at which the key would be inserted into the array: the index of the first element in the range greater than the key, or toIndex if all elements in the range are less than the specified key.
1
2
3
4
if (insertionPoint < 0) {
insertionPoint = ~insertionPoint;
}
// now 0 <= insertionPoint <= toIndex
Maximum Total Beauty of the Gardens
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
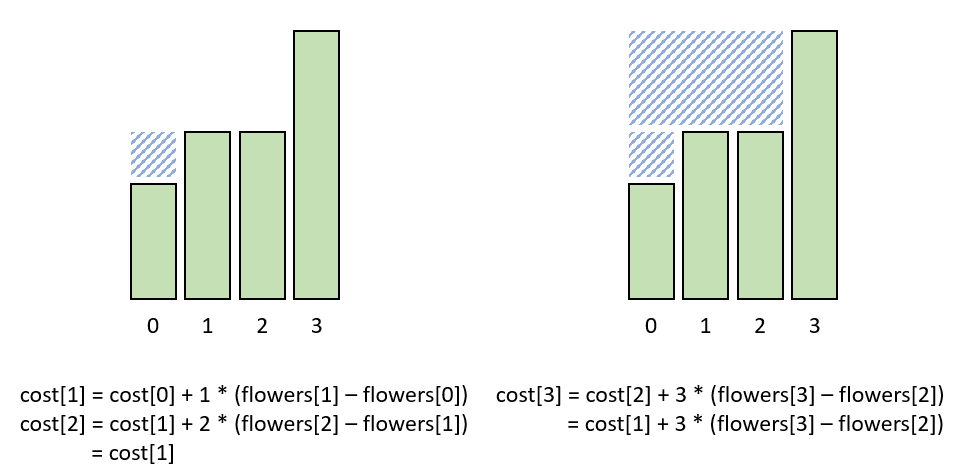
public long maximumBeauty(int[] flowers, long newFlowers, int target, int full, int partial) {
Arrays.sort(flowers);
int n = flowers.length;
// cost[i]: total flowers needed to make flowers[0...(i - 1)] == flowers[i]
long[] cost = new long[n];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
// trims down each garden to at most target flowers
flowers[i] = Math.min(flowers[i], target);
cost[i] = cost[i - 1] + i * (flowers[i] - flowers[i - 1]);
}
// if all gardens are already complete
if (flowers[0] == target) {
return (long)full * n;
}
// if we can make all gardens complete with newFlowers
if (newFlowers >= cost[n - 1] + (target - flowers[n - 1]) * n) {
// all complete vs. all partial (with max possible number of flowers in partial gardens: target - 1)
return (long)full * (n - 1) + Math.max(full, (long)partial * (target - 1));
}
// finds the first partial garden from right to left
int j = n - 1;
while (flowers[j] == target) {
j--;
}
// starting from j-th garden, they are complete
long max = 0;
while (newFlowers > 0) {
// binary searches the i-th garden, where cost[i] <= newFlowers
int index = Arrays.binarySearch(cost, 0, j + 1, newFlowers);
if (index < 0) {
index = ~index - 1;
}
long height = flowers[index] + (newFlowers - cost[index]) / (index + 1);
max = Math.max(max, height * partial + (long)full * (n - j - 1));
newFlowers -= target - flowers[j--];
}
return max;
}
The key is to understand the computation of cost[i]:
Collections
public static <T> int binarySearch(List<? extends T> list, T key, Comparator<? super T> c)
Count Good Triplets in an Array
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
public long goodTriplets(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int n = nums1.length;
// indices[num]: index of element num in nums2
int[] indices = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
indices[nums2[i]] = i;
}
// now the problem becomes: in the array `indices`, for each indices[i]
// counts the number of less elements on the left
// and the number of greater elements on the right
// result = sum(less[i] * greater[i])
// list of sorted indices (in nums2) of visited nums1 elements
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(indices[nums1[0]]);
long count = 0;
// ignores the first and last element
for (int i = 1; i < n - 1; i++) {
// finds the insertion point of index[nums[i]] in the list
// it stands for the number of common elements on the left of nums[i] in both arrays
int insertionPoint = ~Collections.binarySearch(list, indices[nums1[i]]);
list.add(insertionPoint, indices[nums1[i]]);
// common elements on the right
// = n - common elements on the left (= insertionPoint)
// - unique elements in nums1 (= i - insertionPoint)
// - unique elements in nums2 (= indices[nums1[i]] - insertionPoint)
// - self (= 1)
count += (long)insertionPoint * (n - i - indices[nums1[i]] + insertionPoint - 1);
}
return count;
}
For example, nums1 = [2,0,1,3], nums2 = [0,1,2,3]
1
2
3
4
5
indices = [2,0,1,3]
i = 0, list = [2]
i = 1, list = [0, 2], insertionPoint = 0
i = 2, list = [0, 1, 2], insertionPoint = 1
i = 3, list = [0, 1, 2, 3], insertionPoint = 3
This problem is similar to Count of Smaller Numbers After Self, so we can find this insertionPoint (i.e. number of less elements on the left) dynamically by merge sort or Fenwick Tree:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
FenwickTree ft = new FenwickTree(n);
long count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int less = ft.sum(indices[nums1[i]] + 1);
count += (long)less * (n - i - indices[nums1[i]] + less - 1);
ft.add(indices[nums1[i]] + 1, 1);
}
return count;
Minimax
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
public int minCapability(int[] nums, int k) {
int low = 1, high = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
// greedy
// if two adjacent houses are both <= mid, selecting the left house is no worse than the right one
int robbedHouses = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] <= mid) {
robbedHouses++;
i++;
}
}
if (robbedHouses >= k) {
high = mid;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return low;
}
Magnetic Force Between Two Balls
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
public int maxDistance(int[] position, int m) {
Arrays.sort(position);
int low = 0, high = position[position.length - 1] - position[0];
while (low < high) {
int mid = (low + high + 1) >>> 1;
if (condition(position, mid, m)) {
low = mid;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return low;
}
/**
* Counts the max number of balls can be placed into baskets with the given minimum distance.
* This function is monotonically decreasing with respect to d.
* @param position basket postitions
* @param d minimum distance between any two balls
* @return true if number of balls can be places into baskets is no less than m, otherwise false
*/
private boolean condition(int[] position, int d, int m) {
// always places the first ball at position[0]
// this ensures we can place the most balls
int count = 1, curr = position[0];
for (int i = 1; i < position.length; i++) {
if (position[i] - curr >= d) {
count++;
curr = position[i];
}
}
return count >= m;
}
Maximize the Minimum Powered City
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
public long maxPower(int[] stations, int r, int k) {
long low = 0, high = Arrays.stream(stations).asLongStream().sum() + k;
System.out.println(high);
while (low < high) {
long mid = (low + high + 1) >>> 1;
System.out.println(mid);
if (condition(stations, r, k, mid)) {
low = mid;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return low;
}
private boolean condition(int[] stations, int r, int k, long m) {
// sum of powers in the sliding window [i - r, i + r]
// i.e. power of the i-th city
long power = Arrays.stream(stations).asLongStream().limit(r).sum();
int n = stations.length;
int[] additions = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i + r < n) {
power += stations[i + r];
}
if (power < m) {
// required stations to make current center city have at least m power
long delta = m - power;
if (delta > k) {
return false;
}
// builds the additional stations on the right end of the window
// to cover as many cities as possible
additions[Math.min(i + r, n - 1)] += delta;
power = m;
k -= delta;
}
// out of window
if (i - r >= 0) {
power -= stations[i - r] + additions[i - r];
}
}
return true;
}