BFS
Fundamentals
Level traversal. The most common data structure used is Queue. Two rolling Lists or Sets (de-dupe) can also be used, but less common.
Smallest Greater Multiple Made of Two Digits
Implicit BFS
No complex data structure is used.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
public int jump(int[] nums) {
int jumps = 0;
// curr: the farthest start index on the current level.
// in other words, [0, curr] can already be reached by previous levels.
// if start index is greater than `curr`, we should increment the level.
// next: the farthest end index where points on the current level can jump to.
for (int i = 0, curr = 0, next = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// if nums[n - 1] is not always reachable
// (can be commented out for this specific problem)
if (i > next) {
return -1;
}
if (i > curr) {
jumps++;
curr = next;
}
next = Math.max(next, i + nums[i]);
}
return jumps;
}
Depending on the definition of nums[i], the code might need slight modification. e.g., if nums[i] means the farthest reach of each jump, then:
1
next = Math.max(next, i + nums[i]);
should be changed to:
1
next = Math.max(next, nums[i]);
Priority Queue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
private static final int[][] DIRECTIONS = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
public int trapRainWater(int[][] heightMap) {
int m = heightMap.length, n = heightMap[0].length;
Queue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[2]));
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n];
// enqueues border cells
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
pq.offer(new int[] {i, 0, heightMap[i][0]});
pq.offer(new int[] {i, n - 1, heightMap[i][n - 1]});
visited[i][0] = visited[i][n - 1] = true;
}
for (int j = 1; j < n - 1; j++) {
pq.offer(new int[] {0, j, heightMap[0][j]});
pq.offer(new int[] {m - 1, j, heightMap[m - 1][j]});
visited[0][j] = visited[m - 1][j] = true;
}
int volume = 0;
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
// picks the cell with lowest height
int[] cell = pq.poll();
for (int[] d : DIRECTIONS) {
int i = cell[0] + d[0], j = cell[1] + d[1];
if (i >= 0 && i < m && j >= 0 && j < n && !visited[i][j]) {
// if the neighbor is higher,
// computes the amount of water the current can trap by comparing its height with its neighbors'
// then enqueues the neighbor
volume += Math.max(0, cell[2] - heightMap[i][j]);
// if the neighbor is lower, fills the neighbor with the cell's height
// enqueues the neighbor and now it becomes a new border cell
pq.offer(new int[] {i, j, Math.max(heightMap[i][j], cell[2])});
// there might be more than one {i, j, _} nodes in the queue
// but their neighbors won't be processed more than once with the help of `visited` array
visited[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
return volume;
}
In fact, this problem can be solved with Dijkstra’s algorithm, too.
Set
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
public int[] minReverseOperations(int n, int p, int[] banned, int k) {
int[] ans = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(ans, -1);
ans[p] = 0;
Set<Integer> banSet = Arrays.stream(banned).mapToObj(Integer::valueOf).collect(Collectors.toSet());
// sets of unvisited positions
TreeSet<Integer> even = new TreeSet<>(), odd = new TreeSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i != p && !banSet.contains(i)) {
(i % 2 == 0 ? even : odd).add(i);
}
}
// BFS
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(p);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int index = q.poll();
// given k, the parity of the next position of a specific index is certain
var set = (k ^ index) % 2 == 0 ? odd : even;
int[] range = getRange(n, index, k);
var sub = set.subSet(range[0], true, range[1], true);
for (var i : sub) {
ans[i] = ans[index] + 1;
q.offer(i);
}
sub.clear();
}
return ans;
}
private int[] getRange(int n, int index, int k) {
// left most candidate subarray
int l1 = Math.max(0, index - k + 1);
int r1 = l1 + k - 1;
// right most candidate subarray
int r2 = Math.min(n - 1, index + k - 1);
int l2 = r2 - k + 1;
// r[0] and index are symmetric about the center of [l1, l1]
// r[1] and index are symmetric about the center of [l2, l2]
return new int[]{l1 + r1 - index, l2 + r2 - index};
}
Composite Vertex
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
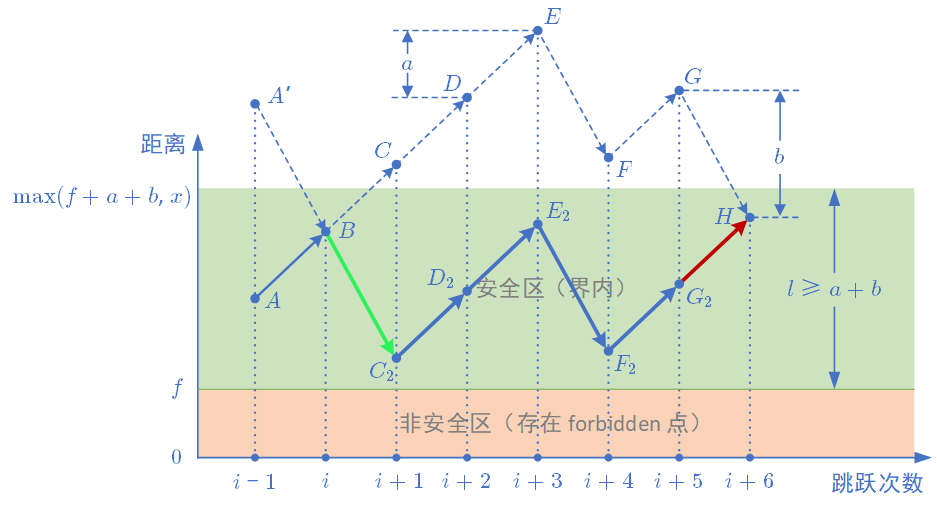
public int minimumJumps(int[] forbidden, int a, int b, int x) {
// as per Bezout's Identity
// if the bug can reach a position, it must be a multiple of gcd(a, b)
// we use an integer to hold two dimensions: position and direction
// since the bug never jumps to negative positions
// we use + to denote "forward", and - to denote "backward"
Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();
// boundary is max(max(forbidden) + a + b, x)
int furthest = x;
for (int p : forbidden) {
visited.add(p); // forward
visited.add(-p); // backward
furthest = Math.max(furthest, p);
}
furthest += a + b;
// position, direction (0: forward, 1: backward)
int[] node = {0, 0};
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(node);
visited.add(0);
int jumps = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
for (int i = q.size(); i > 0; i--) {
node = q.poll();
if (node[0] == x) {
return jumps;
}
int forward = node[0] + a;
if (forward <= furthest && visited.add(forward)) {
q.offer(new int[]{forward, 0});
}
int backward = node[0] - b;
if (node[1] == 0 && backward >= 0 && visited.add(-backward)) {
q.offer(new int[]{backward, 1});
}
}
jumps++;
}
return -1;
}
The proof of the max boundary can be found at here. Credits to @newhar.
Minimum Moves to Reach Target with Rotations
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// {i, j, orientation (horizontal: 0, vertical: 1)}
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
int[] node = {0, 0, 0};
q.offer(node);
boolean[][][] visited = new boolean[n][n][2];
visited[0][0][0] = true;
Shortest Path in a Grid with Obstacles Elimination
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
// {i, j, number of eliminated obstacles}
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
int[] node = new int[]{0, 0, 0};
q.offer(node);
boolean[][][] visited = new boolean[m][n][k + 1];
visited[0][0][0] = true;
1
// {i, j, key mask}
Encode the layout as a String.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public int depthSumInverse(List<NestedInteger> nestedList) {
Queue<NestedInteger> q = new LinkedList<>(nestedList);
int runningSum = 0, sum = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
for (int i = q.size(); i > 0; i--) {
NestedInteger ni = q.poll();
if (ni.isInteger()) {
runningSum += ni.getInteger();
} else {
q.addAll(ni.getList());
}
}
sum += runningSum;
}
return sum;
}
Memoization
Shortest Path with Alternating Colors
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
public int[] shortestAlternatingPaths(int n, int[][] redEdges, int[][] blueEdges) {
// red: 0, blue: 1
List<List<Integer>>[] graph = new ArrayList[2];
for (int i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (var list : graph) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
list.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
}
for (int[] r : redEdges) {
graph[0].get(r[0]).add(r[1]);
}
for (int[] b : blueEdges) {
graph[1].get(b[0]).add(b[1]);
}
int max = 2 * n;
// distance[i][j]: shortest path from 0 to j ending with i-color edge
int[][] distance = new int[2][n];
// distance[][0] == 0
// maximum distance == 2 * n - 3
// it happens when in a path from 0 to target,
// all the intermediate nodes (excluding 0 and target) have an additional self-edge
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
distance[0][i] = max;
distance[1][i] = max;
}
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
// {node, color}
q.offer(new int[]{0, 0});
q.offer(new int[]{0, 1});
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] node = q.poll();
int color = node[1];
for (int neighbor : graph[1 - color].get(node[0])) {
if (distance[1 - color][neighbor] == max) {
distance[1 - color][neighbor] = distance[color][node[0]] + 1;
q.offer(new int[]{neighbor, 1 - color});
}
}
}
int[] answer = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int p = Math.min(distance[0][i], distance[1][i]);
answer[i] = p == max ? -1 : p;
}
return answer;
}
Variants
In the following “maze” model, the neighbors of a node is not adjacent to it.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
private static final int[][] DIRECTIONS = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
public boolean hasPath(int[][] maze, int[] start, int[] destination) {
int m = maze.length, n = maze[0].length;
// stores "stop points"
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(start);
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n];
visited[start[0]][start[1]] = true;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] p = q.poll();
// stops AT destination
if (p[0] == destination[0] && p[1] == destination[1]) {
return true;
}
for (int[] d: DIRECTIONS) {
int r = p[0] + d[0], c = p[1] + d[1];
// keeps rolling until hitting a wall
while (r >= 0 && c >= 0 && r < m && c < n && maze[r][c] == 0) {
r += d[0];
c += d[1];
}
r -= d[0];
c -= d[1];
if (!visited[r][c]) {
q.offer(new int[]{r, c});
visited[r][c] = true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
1
boolean[][] visited -> int[][] distance
Pruning
Symmetry: x -> |x|, y -> |y|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
private List<String> getNeighbors(String source, String target) {
// finds an index i where source[i] != target[i]
char[] arr = source.toCharArray();
int n = arr.length, i = 0;
while (i < n) {
if (arr[i] != target.charAt(i)) {
break;
}
i++;
}
// finds all index j where source[j] == target[i]
// in this case, swapping i and j makes source and target closer
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (arr[j] == target.charAt(i)) {
swap(arr, i, j);
list.add(new String(arr));
swap(arr, i, j);
}
}
return list;
}
Multi-source BFS
Vertex values are updated layer by layer from sources (Expanding)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
private static final int[][] DIRECTIONS = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
public int orangesRotting(int[][] grid) {
int fresh = 0, time = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[i].length; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
fresh++;
}
}
}
int prev = fresh;
while (fresh > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[i].length; j++) {
// oranges that got rotten yesterday
if (grid[i][j] == time + 2) {
for (int[] d : DIRECTIONS) {
fresh -= rot(grid, i + d[0], j + d[1], time);
}
}
}
}
if (fresh == prev) {
return -1;
}
time++;
prev = fresh;
}
return time;
}
private int rot(int[][] grid, int i, int j, int time) {
if (i < 0 || i >= grid.length || j < 0 || j >= grid[i].length || grid[i][j] != 1) {
return 0;
}
grid[i][j] = time + 3;
return 1;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
private static final int[][] DIRECTIONS = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
public int[][] highestPeak(int[][] isWater) {
int m = isWater.length, n = isWater[0].length;
// enqueues all sources
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
int[][] height = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (isWater[i][j] == 1) {
height[i][j] = 0;
q.offer(new int[]{i, j});
} else {
height[i][j] = -1;
}
}
}
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] cell = q.poll();
int r = cell[0], c = cell[1];
for (int[] d : DIRECTIONS) {
int nr = r + d[0], nc = c + d[1];
if (nr >= 0 && nr < m && nc >= 0 && nc < n && height[nr][nc] == -1) {
height[nr][nc] = height[r][c] + 1;
q.offer(new int[]{nr, nc});
}
}
}
return height;
}
In the following two problems, BFS starts from gates/buildings/… to empty places. In most cases, it’s optimal because we can use memoization.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
private static final int[][] DIRECTIONS = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
public void wallsAndGates(int[][] rooms) {
int m = rooms.length, n = rooms[0].length;
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (rooms[i][j] == 0) {
q.offer(new int[]{i, j});
}
}
}
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] p = q.poll();
int r = p[0], c = p[1];
for (int[] d : DIRECTIONS) {
int i = r + d[0], j = c + d[1];
if (i >= 0 && i < m && j >= 0 && j < n && rooms[i][j] == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
// each gate only checks the areas within 1 space
// then these emptry rooms are marked and enqueued, so on and so forth.
// it's like a few water waves expanding
rooms[i][j] = rooms[r][c] + 1;
q.offer(new int[]{i, j});
}
}
}
}
Shortest Distance from All Buildings
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
private static final int[][] DIRECTIONS = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
public int shortestDistance(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length, buildingCount = 0;
// distances[i][j]: total distances to this empty land
// buildings[i][j]: total buildings to this empty land
int[][] distances = new int[m][n], buildings = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// from each building to empty lands
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
buildingCount++;
// BFS
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
int[] node = new int[]{i, j};
q.offer(node);
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n];
visited[i][j] = true;
int steps = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
for (int k = q.size(); k > 0; k--) {
node = q.poll();
int r0 = node[0], c0 = node[1];
if (grid[r0][c0] == 0) {
distances[r0][c0] += steps;
buildings[r0][c0]++;
}
// traverses the next cells which are not blockages.
for (int[] d : DIRECTIONS) {
int r = r0 + d[0], c = c0 + d[1];
if (r >= 0 && c >= 0 && r < m && c < n && !visited[r][c] && grid[r][c] == 0) {
visited[r][c] = true;
q.offer(new int[]{r, c});
}
}
}
steps++;
}
}
}
}
// checks all empty lands with buildings count == buildingCount
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (buildings[i][j] == buildingCount) {
min = Math.min(min, distances[i][j]);
}
}
}
return min == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : min;
}
Bidirectional BFS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
if (!wordList.contains(endWord)) {
return 0;
}
Set<String> dict = new HashSet<>(wordList);
Set<String> beginSet = new HashSet<>(), endSet = new HashSet<>();
beginSet.add(beginWord);
endSet.add(endWord);
int len = 1;
Set<String> visited = new HashSet<>();
// in each iteration, builds up the elements in beginSet
while (!beginSet.isEmpty() && !endSet.isEmpty()) {
// always makes beginSet the smaller one by swapping
if (beginSet.size() > endSet.size()) {
Set<String> tmp = beginSet;
beginSet = endSet;
endSet = tmp;
}
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>(); // next level of beginSet
for (String word : beginSet) {
char[] chs = word.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {
for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++) {
char old = chs[i];
chs[i] = c;
String target = String.valueOf(chs);
// target is already visited in the other set
if (endSet.contains(target)) {
return len + 1;
}
if (!visited.contains(target) && dict.contains(target)) {
set.add(target);
visited.add(target);
}
chs[i] = old;
}
}
}
beginSet = set;
len++;
}
return 0;
}
+ Algorithms/Data Structures
+ Priority Queue
+ BFS
Second Minimum Time to Reach Destination
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
private static final int MAX_NUM_NODES = (int)1e4;
public int secondMinimum(int n, int[][] edges, int time, int change) {
List<Integer>[] graph = new List[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int[] e : edges) {
graph[e[0]].add(e[1]);
graph[e[1]].add(e[0]);
}
// minSteps[i]: minimum steps from vertex i to vertex n
int[] minSteps = new int[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(minSteps, MAX_NUM_NODES + 1);
int node = n;
minSteps[node] = 0;
// first BFS
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(node);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
node = q.poll();
for (int neighbor : graph[node]) {
if (minSteps[neighbor] == MAX_NUM_NODES + 1) {
minSteps[neighbor] = minSteps[node] + 1;
q.offer(neighbor);
}
}
}
// if the minimum number of steps from 1 to n is k
// then the second minimum time is either:
// k + 2 (goes back-and-forth once) or
// k + 1 (takes a detour)
// second BFS
int steps = minSteps[node = 1] + 2;
q.offer(node);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
node = q.poll();
for (int neighbor : graph[node]) {
// there exists a detour
if (minSteps[neighbor] == minSteps[node]) {
return calculateTime(steps - 1, time, change);
}
// pruning: enqueues only the neighbors that are on the shortest path from current node to n
// in fact, there are only 3 possibilities:
// 1. minSteps[neighbor] == minSteps[node]
// 2. minSteps[neighbor] == minSteps[node] - 1
// 3. minSteps[neighbor] == minSteps[node] + 1
if (minSteps[neighbor] == minSteps[node] - 1) {
q.offer(neighbor);
}
}
}
return calculateTime(steps, time, change);
}
private int calculateTime(int steps, int time, int change) {
int total = 0;
while (steps-- > 0) {
// traffic light switches (to red), waits another change
if ((total / change) % 2 == 1) {
total = (total / change + 1) * change;
}
total += time;
}
return total;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
private static final int[][] DIRECTIONS = {{-1, 0}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}};
public int maximumMinutes(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
// personMinutes[i][j]: the earliest time you will reach the cell (i, j)
int[][] personMinutes = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
Arrays.fill(personMinutes[i], -1);
}
personMinutes[0][0] = 0;
int minute = 0;
int[] cell = {0, 0};
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(cell);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
minute++;
for (int i = q.size(); i > 0; i--) {
cell = q.poll();
for (int[] d : DIRECTIONS) {
int r = cell[0] + d[0], c = cell[1] + d[1];
if (r >= 0 && r < m && c >= 0 && c < n && personMinutes[r][c] < 0 && grid[r][c] == 0) {
personMinutes[r][c] = minute;
q.offer(new int[]{r, c});
}
}
}
}
// fireMinutes[i][j]: the earliest time the person will reach the cell (i, j)
int[][] fireMinutes = new int[m][n];
minute = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
fireMinutes[i][j] = -1;
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
q.offer(new int[]{i, j});
fireMinutes[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
minute++;
for (int i = q.size(); i > 0; i--) {
cell = q.poll();
for (int[] d : DIRECTIONS) {
int r = cell[0] + d[0], c = cell[1] + d[1];
if (r >= 0 && r < m && c >= 0 && c < n && fireMinutes[r][c] < 0 && grid[r][c] == 0) {
fireMinutes[r][c] = minute;
q.offer(new int[]{r, c});
}
}
}
}
// you can't reach the safehouse
if (personMinutes[m - 1][n - 1] < 0) {
return -1;
}
// fire can't spread to the safehouse
if (fireMinutes[m - 1][n - 1] < 0) {
return (int)1e9;
}
// the fire spreads to it earlier than you
if (personMinutes[m - 1][n - 1] > fireMinutes[m - 1][n - 1]) {
return -1;
}
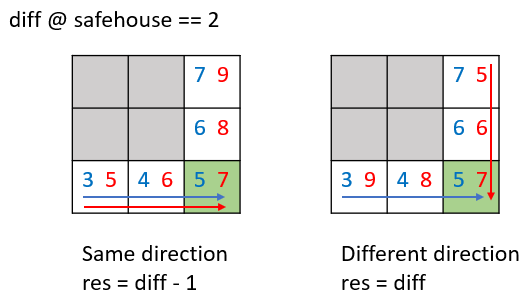
// on a valid path from start to safehouse, diff = (fireMinutes - personMinutes) is non-increasing
// suppose you and the fire meet at a cell (i, j), and diff == 2
// it means you are ahead of the fire by 2 minutes.
// from now on, the fire can conservatively follow your trace so the diff remains as 2.
// there possibly exists a better strategy for the fire at drive the diff down even further.
// diff at (m - 2, n - 1) > diff at safehouse means you and fire came from different directions
// (otherwise the diff at this west neighbor would be == diff at safehouse)
// same as the north neighbor.
// in this case, you meet the fire right at the safehouse.
//
// otherwise, diff at west and north neighbors are the same as the safehouse,
// which means you and fire meet right before the safehouse.
// (the fire follows you all the way)
// in this case, you need to wait one minute shorter
int diff = fireMinutes[m - 1][n - 1] - personMinutes[m - 1][n - 1];
return personMinutes[m - 2][n - 1] >= 0 && personMinutes[m - 1][n - 2] >= 0 &&
(fireMinutes[m - 2][n - 1] - personMinutes[m - 2][n - 1] > diff ||
fireMinutes[m - 1][n - 2] - personMinutes[m - 1][n - 2] > diff) ? diff : diff - 1;
}
Another solution is to compute fireMinutes, and binary searches the max wait time so that you can reach the safehouse.
+ DFS
Minimum Cost to Make at Least One Valid Path in a Grid
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
// index = grid[i][j] - 1
private static final int[][] DIRECTIONS = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
public int minCost(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
int[][] costs = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
Arrays.fill(costs[i], -1);
}
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>(); // {r, c}
int cost = 0;
// finds all reachable cells
dfs(grid, costs, 0, 0, cost, q);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
cost++;
for (int i = q.size(); i > 0; i--) {
int[] cell = q.poll();
int r = cell[0], c = cell[1];
// modifies the sign to all possible directions
for (int[] d : DIRECTIONS) {
dfs(grid, costs, r + d[0], c + d[1], cost, q);
}
}
}
return costs[m - 1][n - 1];
}
// DFS finds all reachable cells.
// all sign modifications allowed with this cost have been completed in its preceding BFS,
// so no sign can be modified in DFS.
private void dfs(int[][] grid, int[][] costs, int r, int c, int cost, Queue<int[]> q) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
// costs[r][c] >= 0 means this cell has been visited with lower or equal cost
if (r < 0 || r == m || c < 0 || c == n || costs[r][c] >= 0) {
return;
}
costs[r][c] = cost;
// adds newly visited cell to the level
q.offer(new int[]{r, c});
// no sign modification is allowed, so just follow the sign
int[] d = DIRECTIONS[grid[r][c] - 1];
dfs(grid, costs, r + d[0], c + d[1], cost, q);
}
Bit Mask
Shortest Path Visiting All Nodes
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
public int shortestPathLength(int[][] graph) {
int n = graph.length;
Set<String> visited = new HashSet<>();
// {label, mask}
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
q.offer(new int[]{i, 1 << i});
visited.add(i + "#" + (1 << i));
}
int level = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
for (int i = q.size(); i > 0; i--) {
int[] node = q.poll();
if (node[1] == (1 << n) - 1) {
return level;
}
for (int neighbor : graph[node[0]]) {
int[] next = {neighbor, node[1] | (1 << neighbor)};
if (visited.add(next[0] + "#" + next[1])) {
q.offer(next);
}
}
}
level++;
}
return level;
}